Breast Imaging: A Core Review (37 page)
Read Breast Imaging: A Core Review Online
Authors: Biren A. Shah,Sabala Mandava
Tags: #Medical, #Radiology; Radiotherapy & Nuclear Medicine, #Radiology & Nuclear Medicine

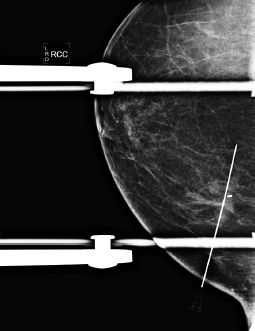
A. The patient goes to the OR; procedure is complete.
B. Return to the ML view for repositioning.
C. Retract the needle slightly, and take another image.
D. Place the wire, and take another image.
21
A specimen radiograph postwire localization was performed. A new nurse in the OR calls into the reading room with some questions. Which of the following is most accurate regarding specimen radiographs?
A. Routinely performed after the patient leaves the OR
B. Only performed for masses
C. Accurately determines if the surgical margins are negative
D. Performed with magnification
22
When performing a stereotactic biopsy, what is stroke margin?
A. The distance from the image receptor to the tip of the needle postfire
B. The distance from the image receptor to the tip of the needle prefire
C. The distance of the lesion to the tip of the needle postfire
D. The distance of the lesion to the tip of the needle prefire
23
The image shown below is an ultrasound of the axilla in a patient with biopsy-proven breast cancer. A core needle biopsy was performed. Pathology shows benign reactive lymph node. The patient will receive which of the following procedures along with her lumpectomy?
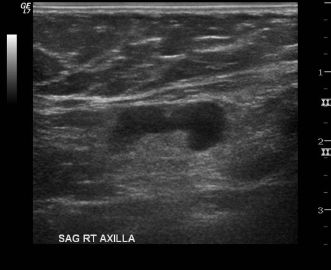
A. None
B. Rebiopsy is indicated prior to surgery.
C. Sentinel lymph node biopsy
D. Axillary dissection
24
Regarding stereotactic-guided breast biopsy, which of the following is correct?
A. A negative stroke margin is necessary to perform the biopsy.
B. Postprocedure mammogram is not necessary.
C. The most common complication is infection.
D. Specimen radiograph is performed to evaluate for adequate sampling.
E. The optimal needle approach is lateral.
25
Pathology for a core biopsy of this lesion imaged showed florid epithelial hyperplasia. What is the appropriate recommendation?
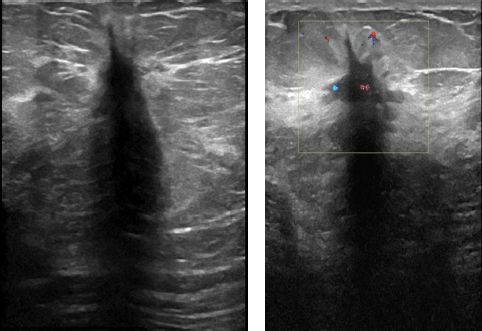
A. Surgical excisional biopsy
B. Breast-specific gamma imaging (BSGI)
C. Breast MRI
D. Follow-up diagnostic ultrasound in 6 months
26
Which of the following is a contraindication to whole-breast radiation therapy?
A. Axillary adenopathy
B. Collagen vascular disease
C. Residual microscopic disease
D. Younger women
27
The maximum dose of 1% lidocaine with epinephrine used for deep local anesthesia is
A. 7 mg/kg body weight, not to exceed 500 mg
B. 7 mg/kg body weight, not to exceed 1,000 mg
C. 10 mg/kg body weight, not to exceed 500 mg
D. 10 mg/kg body weight, not to exceed 1,000 mg
28a
A 47-year-old female with history of nipple discharge is referred from the breast surgeon for ductography. Which of the following is correct?
A. Ductography is indicated for single pore spontaneous nipple discharge.
B. Ductography is the procedure used to biopsy an intraductal mass.
C. Suspicious discharge includes spontaneous unilateral green or white discharge.
D. The standard dose of contrast used for ductography is 5 mL.
28b
The following images are available from this patient’s ductogram. What is the next best step in patient management?
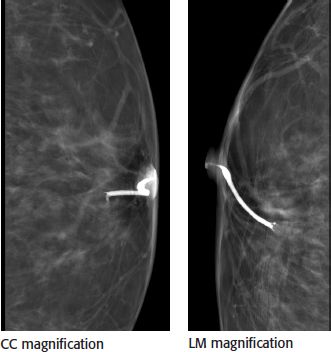
A. Stereotactic breast biopsy
B. Diagnostic breast MRI
C. Repeat ductogram due to artifact
D. Surgical breast biopsy
29
Which of the following statements concerning percutaneous biopsy is correct?
A. Correlation between pathology results and imaging studies does not have to be done for asymmetries.
B. Surgical excision is always recommended for atypical ductal hyperplasia and atypical lobular hyperplasia.
C. Pseudoaneurysms can occur in the breast after core biopsy.
D. Markers generally do not migrate after completion of stereotactic biopsy.
30
During galactography, how much contrast material is injected into the duct?
A. <0.3 mL
B. 0.3 to 1.0 mL
C. 2 to 4 mL
D. 3 to 6 mL
31
A stereotactic biopsy was performed on a 47-year-old patient. The pathology results are atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH). What is the appropriate recommendation?
A. Surgical excision
B. MRI
C. 6-month follow-up
D. Repeat stereotactic biopsy
32
A 39-year-old female is scheduled for a contrast-enhanced breast MRI for high-risk screening evaluation. She undergoes laboratory testing for renal function due to her history of diabetes mellitus. Her laboratory results are creatinine of 1.8 mg/dL and a calculated GFR of 28 mL/min/1.73 m 2 . No prior laboratory data are available to review. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the evaluation of this patient?
A. Consult with referring physician, and discuss risk–benefit ratio. If the examination is essential, use the lowest possible contrast dose as possible.
B. Proceed with the breast MRI without use of gadolinium-based contrast agent.
C. Proceed with the breast MRI using a standard dose of gadolinium-based contrast agent.
D. Cancel the breast MRI study.
33
Four days after a screening mammogram, a 40-year-old female discovers she is pregnant and estimates that the fetus is in its 3rd week of gestation. Which of the following is the most appropriate response regarding the amount of radiation the fetus received from the mammogram exam?
A. The fetus is unharmed because there was no radiation exposure.
B. The fetus is at potential risk of embryologic demise.
C. The fetus is at negligible risk for potential radiation-induced malformation of organs.
D. The child will have a 1% risk of developing severe mental retardation.
E. There is a high likelihood of a radiation-induced malformation of organs.
34
A 43-year-old female, with no known allergies or past medical condition, underwent an uneventful right breast stereotactic core needle biopsy in the morning. After needle biopsy, hemostasis was successfully achieved, and the patient was sent home. The patient returns to the radiology department complaining of right breast pain at the breast biopsy site. There is no oozing or unexpected bleeding or palpable lump at the biopsy site. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial management of the patient’s breast pain?
A. Give a prescription of Tylenol 3 (acetaminophen with codeine) for the patient to take as needed.
B. Give a prescription of Vicodin (acetaminophen with hydrocodone) for the patient to take as needed.
C. Advise the patient to take acetaminophen initially and then every 6 hours as needed, up to 4/d.
D. Advise the patient to take aspirin initially and then every 4 to 6 hours as needed, up to 3/d.
35
Which of the following situation can make stereotactic biopsy difficult, either requiring special repositioning of the patient or technically impossible?
A. Patient with breast thickness of 3 cm on the craniocaudal and breast thickness of 3.5 cm on mediolateral oblique view
Other books
Kept by Field, Elle
Days of Desire by India T. Norfleet
Courtship of the Cake by Jessica Topper
A Little History of Literature by John Sutherland
Taste of Darkness (An Avry of Kazan Novel - Book 3) by Snyder, Maria V.
Running in Heels by Anna Maxted
Cherringham--Thick as Thieves by Neil Richards
The Thief's Tale by Jonathan Moeller
Murder Ring (A DI Geraldine Steel Mystery) by Leigh Russell
To Love a Lord by Christi Caldwell