Caesar's Messiah: The Roman Conspiracy to Invent Jesus:Flavian Signature Edition (14 page)
Read Caesar's Messiah: The Roman Conspiracy to Invent Jesus:Flavian Signature Edition Online
Authors: Joseph Atwill

Thus, the New Testament satires of events from
Wars of the Jews
were not haphazardly sequenced, as I had originally assumed, but were placed in the same sequence as the events they satirized. In other words, the entire outline of Jesus’ ministry, as recorded within the New Testament, was designed as a typological prophecy of Titus’ campaign through Judea.
For clarification, I present the following table of the five conceptual parallels in sequence shown thus far:
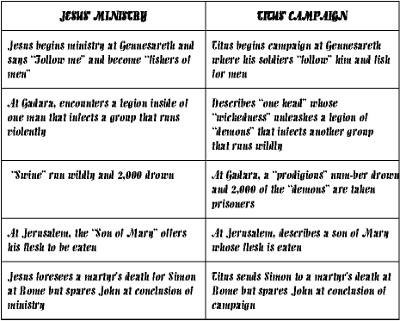
The Gospels’ stories concerning “fishing for men,” a “legion” of demons coming out of one man to infect many, a human Passover lamb, three crucified one survives, and a conclusion where Simon is condemned and John spared, can be seen as satirizing very few works of literature. It is, therefore, quite implausible that the New Testament describes, by chance, so many episodes that can be seen as satirizing the events in a single book.
While it is possible to argue that each New Testament episode that appears to satirize an event in
Wars of the Jews
does so accidentally, if that were the case these accidents would occur in a random sequence and at random locations. It was not required that Jesus use the expression “fishers of men” while standing on the beach at Gennesareth, any more than it was required that he meet the demoniac at Gadara. Nor was it necessary for him to offer his flesh at Jerusalem, or to condemn Simon but spare John at the conclusion of his ministry. The fact that these five events occur in the New Testament in the same sequence as their parallel events in
Wars of the Jews,
strongly supports the contention that one work was created with the other in mind.
Therefore, the parallel sequences, concepts, and locations make the authors’ intent clear. In the same way that they show the first savior of Israel, Moses, to have been the “type” for Jesus, the second savior of Israel, through their parallel infancy experiences, they also “prove” that Titus is the last and greatest “savior” because Jesus’ ministry is the “type” for Titus’ campaign through Judea.
Finally, the parallel sequences of Jesus’ and Titus’ “ministries” must be considered in the context of their historical overlaps. As I noted above, Jesus predicted that a “Son of God” would come to Judea before the generation that crucified him had passed away, then encircle Jerusalem with a wall and destroy the temple. Titus is the only individual in history who can be seen as having fulfilled these prophecies.
Such a
combination
of historical singularities could not occur by chance. This is self-evident and the only plausible explanation for the similar story lines is that these parts of Jesus’ ministry were deliberately created to parallel Titus’ campaign through Judea. I will demonstrate this beyond any doubt in the next chapter.
History has shown, of course, that the parallels between the two “Sons of God” are not easy to see. Within the Flavian court however, where “foreign cults in Rome” were carefully scrutinized and knowledge of Titus’ exploits was common, those responsible for overseeing the Empire’s religions would have recognized the satirical parallels between Jesus and Titus and seen them as cuttingly humorous.
The purpose of these parallels, moreover, was not merely to create an amusing satire for patricians. I will show in the following chapter that the authors of the New Testament use parallelism to create a story entirely different from the one that appears on its surface—a story that reveals the hidden identity of the “Jesus” who interacts with the disciples at the conclusion of the Gospels.
Furthermore, understanding that Jesus’ ministry shares a parallel story line and characters with Titus’ campaign, creates a new way to understand the New Testament. Simply moving the events of Jesus’ ministry forward forty years in time and comparing them to the events of Titus’ campaign reveals their satirical meaning. For example, whoever put Jesus’ prophecy about the fate of Simon and John at the conclusion of the Gospel of John, did so solely to have the conclusion of the Gospels ironically mirror the end of Titus’ campaign. The discussion between Jesus and Simon could have occurred at any time during Jesus’ ministry, or been recorded in any of the other Gospels, or not been included at all, since it contains no important theological ideas.
Another example that this method reveals is the satirical basis for Simon’s nickname, Peter, which in Greek is
Petros
, meaning “rock” or “stone.” It is a derisive joke relating to Josephus’ description of the circumstance of the real Simon’s capture.
As stated above, in trying to escape Roman-occupied Jerusalem, Simon fled into a subterranean cavern with a group of
stonecutters
and attempted to dig an escape passage. Unable to carve through rock and out of food, he was forced to surrender. He did so in an extraordinary fashion. Josephus writes:
Simon, thinking he might be able to astonish and elude the Romans, put on a white frock, and buttoned upon him a purple cloak, and appeared out of the ground in the place where the temple had formerly been.
81
The humor is dark and subtle. In the ironic logic of the New Testament’s Simon’s nickname, “stone” satirizes Josephus’ depiction of Simon being captured with a group of stonecutters, who, of course, cut “stone.” As he came “out of the ground in the place where the temple had formerly been” he was, therefore, the first “stone” upon which the new “temple,” Christianity, was to be built. Once again, though Jesus appears to have spoken metaphorically when he tells Simon that he is the “stone” upon which he will build a new church that will replace Judaism, Josephus records an event showing another, sardonic, meaning to Jesus’ words.
And I declare to you that you are Peter, and that upon this Stone I will build my Church …
Matt. 16:18
The depiction of Simon coming out of a cavern, that is a “tomb” and contains a group of stonecutters, also provides satirical confirmation of the premise that Simon the Apostle and the demoniac of Gadara were both lampoons of Simon the leader of the Jewish rebellion. This is because the wry humor regarding “stonecutters” creates a parallel between the demoniac of Gadara who was “cutting himself with stones” and the rebel leader Simon. And since the passages are parallel, the unnamed character in one would have the same name as his named “type” in the other; in this case “Simon” is the name of one of the demoniacs of Gadara.
Understanding this simple point of logic enables a reader to learn the names of many of the unnamed characters in the New Testament and
Wars of the Jews,
and the real identity of Jesus. I will also show that far from being unusual, the use of intertextual parallels to exchange information between passages was commonplace in the Judaic literature of this era.
The New Testament’s black comedy theme regarding “rock” and “stone” appears to be satire on a well-known metaphorical theme found throughout the Dead Sea Scrolls, that of the “foundation of rock.” In the following example from the Thanksgiving Hymn, notice that the author sees himself, like the rebel leader Simon, as entering a “fortified city” and “seeks refuge behind a high wall.”
But I shall be as one who enters a fortified city,
As one who seeks refuge behind a high wall
Until deliverance (comes);
I will (lean on) Thy truth; O my God.
For Thou wilt set the foundation on rock
And the frameworks by the measuring cord of justice;
And the tried stones {Thou will lay}
82
The black comedy logic that links the New Testament to
Wars of the Jews
also makes clear the basis for the epithet of the Apostle John, which is “the disciple whom Jesus loved.
”
John was the “loved disciple” because he was the captive leader whom Titus spared. Further, the real meaning of Jesus’ criticism of his disciples—for example, his describing the Apostles “Simon” and “John” as having demons—is now also apparent. Having maliciously satirized the leaders of the messianic movement as Jesus’ Apostles, the Roman authors of the New Testament then “record” Jesus lecturing his Apostles on their wickedness.
In the Gospel of Luke there is a passage that warns Simon of his being possessed by “Satan” and reiterates the concept that Simon is going to prison and to death “with” Jesus. It also repeats the theme of the demoniac of Gadara (Simon), who returns to his true self after Satan has been repelled. It is another example of Jesus making statements that seem metaphoric but have literal and ironic meaning when read in conjunction with
Wars of the Jews.
“Simon” did indeed go with his “master” to prison and death, his “master” being Titus. Though in the past the following passage has mystified scholars, its meaning is now clear.
“Simon, Simon, I tell you that Satan has obtained permission to have all of you to sift as wheat is sifted.
“But ‘I’ have prayed for ‘you’ that your faith may not fail, and you, when at last you have come back to your true self, must strengthen your brethren.”
“Master,” replied Peter, “with you I am ready to go both to prison and to death.”
Luke 22:31-33
Continuing this black comedy theme in the Gospel of Matthew, Jesus actually calls the Apostle Simon “Satan.” His strange remark about the founder of his church is rendered coherent when one understands that Jesus is referring, in the Roman context, to the rebel Simon. The reader will note that the mysteriousness of many of Jesus’ sayings disappears when they are understood within the context I suggest. In the passage, Jesus repeats the command to Simon that he gives at the conclusion of the Gospel of John above. That is, to “follow me” with a cross to your doom.
And Peter took him and began to rebuke him, saying, “God forbid, Lord! This shall never happen to you.”
But he turned and said to Peter, “Get behind me, Satan! You are a hindrance to me; for you are not on the side of God, but of men.”
Then Jesus told his disciples, “If any man would come after me, let him deny himself and take up my cross and follow me.
“For whoever would save his life will lose it, and whoever loses his life for my sake will find it.”
Matt. 16:22–25
In the passage above from Matthew, notice that Jesus tells his disciples to “take up his cross” and follow. In the passage below from Luke, we learn that in fact “Simon,” called a “Cyrenaean,” did indeed “take up his cross” and “follow” Jesus. Notice how deliberately the author conveys the idea that a “Simon” “followed” Jesus with a cross.
As soon as they led Him away, they laid hold on one Simon, a Cyrenaean, who was coming in from the country, and on his shoulders they put the cross, for him to carry it behind Jesus.
Luke 23:26
The structure of the dark humor involved in Simon’s “following with a cross” is familiar. If one interprets Jesus’ words metaphorically they can be seen to have a spiritual meaning, but if interpreted literally they are black comedy.
The Apostle Paul is also engaged in the lampooning of Simon’s execution.
But when Cephas (
Simon
) came to Antioch I opposed him to his face, because he stood condemned.
Gal 2:11
The strange tale of Simon’s three denials of Jesus is also part of the sequence of events shared by the New Testament and
Wars of the Jews
. The tale is one of the most famous stories in the New Testament and is found in all four Gospels.
The maid who kept the door said to Peter, “Are not you also one of this man’s disciples?” He said, “I am not.” …
Now Simon Peter was standing and warming himself. They said to him, “Are not you also one of his disciples?” He denied it and said, “I am not.”
One of the servants of the high priest, a kinsman of the man whose ear Peter had cut off, asked, “Did I not see you in the garden with him?”
Peter again denied it; and at once the cock crowed.
John 18:17, 25-27