Delphi Complete Works of Sir Arthur Conan Doyle (Illustrated) (1298 page)
Read Delphi Complete Works of Sir Arthur Conan Doyle (Illustrated) Online
Authors: SIR ARTHUR CONAN DOYLE

It may help the reader’s comprehension of the sequence sequence of events, and of the desperate nature of this second Battle of Ypres, if a short resume be here given of the happenings upon the various dates. A single day of this contest would have appeared to be a considerable ordeal to any troops. It is difficult to realise the cumulative effect when such blows fell day after day and week after week upon the same body of men. The more one considers this action the more remarkable do the facts appear.
April 22.
Furious attack upon the French and Canadians. Germans gain several miles of ground, eight batteries of French guns, and four heavy British guns by the use of poison-gas. The Canadians stand firm.
April 23.
Canadians hold the line. Furious fighting. French begin to re-form. Reserves from the Twenty-seventh and Twenty-eighth British Divisions, 13th Brigade, and cavalry buttress up the line.
April 24.
Desperate fighting. Line pushed farther back, and Germans took about a thousand prisoners. Line never broken.
April 25.
Battle at its height. 50th Northern Territorial Division come into the fight. 10th Regular Brigade come up. Canadians drawn out. The French advancing.
April 26.
11th Regular Brigade thrown into the fight. Also the Lahore Division of Indians. Trenches of Twenty-eighth Division attacked.
April 27.
The French made some advance on the left. There was equilibrium on the rest of the line. Hard fighting everywhere.
April 28.
The enemy still held, and his attack exhausted for the moment. French made some progress.
May 1.
British 12th Brigade came into line.
May 2.
Renewed German assault on French and British, chiefly by gas. Advance held back with difficulty by the Fourth Division.
May 3 and 4.
Contraction of the British position, effected without fighting, but involving the abandonment of two miles of ground at the north- eastern salient.
May 5.
German attack upon Fourth Division.
May 6.
Attack still continued.
May 7.
Artillery preparation for general German attack.
May 8.
Furious attack upon Fourth, Twenty-eighth, and Twenty- seventh British Divisions. Desperate fighting and heavy losses. The British repulsed the attack on their left wing (Fourth Division), but sustained heavy loss on centre and right.
May 9.
Very severe battle continued. British left held its ground, but right and centre tended to contract.
May 10.
Fighting of a desperate character, falling especially upon the Twenty-seventh Division.
May 11.
Again very severe fighting fell upon the Twenty-seventh Division on the right of the British line. Losses were heavy, and there was a slight contraction.
May 12.
Readjustment of British line. Two divisions of cavalry put in place of Twenty-eighth Division. Furious artillery attack, followed by infantry advance. Cavalry and Twenty-seventh Division terribly punished. Very heavy losses, but the line held. Fourth Division fiercely engaged and held its line.
May 13.
The Germans exhausted. The attack ceased. Ten days of mutual recuperation.
May 24.
Great gas attack. Fourth Division on left had full force of it, lost heavily, but could not be shifted. In the evening had to retire five hundred yards for the first time since the fighting began. General result of a long day of furious fighting was some contraction of the British line along its whole length, but no gap for the passage of the enemy. This may be looked upon as a last despairing effort of the Germans, as no serious attempt was afterwards made that year to force the road to Ypres.
Such, in a condensed form, was the record of the second Battle of Ypres, which for obstinacy in attack and inflexibility in defence can only be compared with the first battle in the same section six months before. Taking these two great battles together, their result may be summed up in the words that the Germans, with an enormous preponderance of men in the first and of guns in the second, had expended several hundred thousand of their men with absolutely no military advantage whatever.
V. THE BATTLE OF RICHEBOURG FESTUBERT
May 9-24
The new attack — Ordeal of the 25th Brigade — Attack of the First Division — Fateful days — A difficult situation — Attack of the Second Division — Attack of the Seventh Division — British success — Good work of the Canadians — Advance of the Forty- seventh London Division — The lull before the storm
WHILST this desperate fighting was going on in the north a very extensive and costly operation had been begun in the south, a great attack being made by the First Army, with the main purpose of engaging the bourg Festubert German troops and preventing them from sending help to their comrades, who were hard pressed by the French near Arras. In this the movement was entirely successful, but the direct gain of ground was not commensurate with the great exertions and losses of the Army. For some days the results were entirely barren, but the patient determination of Sir John French and of Sir Douglas Haig had their final reward, and by May 25, when the movement had been brought to a close, there had been a general advance of
Both in the north and in the south the special attack was opened by a sudden and severe bombardment, which lasted for about forty minutes. This had been the prelude to the victory of Neuve Chapelle, but in the case of Neuve Chapelle the British attack had been a complete surprise, whereas in this action of May 9 there is ample evidence that the Germans were well informed as to the impending movement, and were prepared for it. Their trenches were very deep, and more vulnerable to high explosives, in which we were deficient, than to shrapnel. None the less, the bombardment was severe and accurate, though, as it proved, insufficient to break down the exceedingly effective system of defence, based upon barbed wire, machine guns, and the mutual support of trenches.
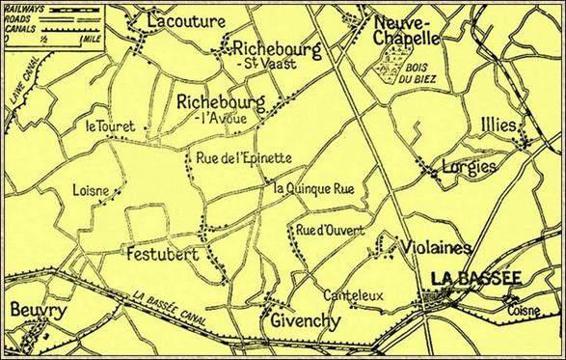
Richebourg District
The attack in the north was confided to Lowry-Cole’s 25th Brigade, supported by the remainder of the Eighth Division. This brigade consisted of the 1st Irish Rifles, 2nd Berkshires, 2nd Rifle Brigade, 2nd Lincoln, and two Territorial battalions the 1st London and the 13th London (Kensington), The latter regiment was given a special task, which was to seize and hold a considerable mine-crater upon the left of the line. The rest of the brigade were ordered at 5:30 to charge the German trenches, which was done with the greatest dash and gallantry. Through a terrific fire of rifles and machine-guns the wave of men rolled forward, and poured into the trench, the 1st Irish Rifles and the 2nd Rifle Brigade leading the assault. It was found, however, that further progress could not be made. As the men sprang over the parapets they were mowed down in an instant. Long swathes of our dead marked the sweep of the murderous machine-guns. The Brigadier himself with his Brigade-major at his heels, sprang forward to lead the troops, but both were shot down in an instant, Lowry-Cole being killed and Major Dill badly wounded. It was simply impossible to get forward. No bravery, no perseverance, no human quality whatever could avail against the relentless sleet of lead. The 1st Londons coming up in support deployed and advanced over
“These God-like fools!” was the striking phrase of a generous German who observed the thin ranks sauntering back under a crushing fire, with occasional halts to gather up their wounded. The casualty figures show how terrific was the ordeal to which the men had been exposed. The Irish Rifles lost the very heavy numbers of 9 officers killed, 13 wounded, and 465 men out of action. The total of the 2nd Rifle Brigade was even more terrible, working out as 21 officers and 526 men dead or wounded. The figures of the 2nd Berkshires and of the 2nd Lincolns were heavy, but less disastrous than those already quoted. The former lost 20 officers and 263 men, the latter 8 officers and 258 men. The 24th Brigade (Oxley) which, had supported the 25th, and had also reached the first trenches, endured losses which were almost as disastrous. The 2nd East Lancashires lost 19 officers and 435 men; the 1st Sherwood Foresters, 17 officers and 342 men; the 2nd Northamptons, 12 officers, and 414 men; the 5th Black Watch, 8 officers and 140 men. The losses of the 23rd Brigade, which remained in support, were by no means light, for the Scottish Rifles lost 12 officers and 156 men; while the 2nd Devons lost 7 officers and 234 men. Altogether the Eighth Division lost 4500 men, a single brigade (the 25th), accounting for 2232 of these casualties. Deplorable as they are, these figures must at least show that officers and men had done all that could be attempted to achieve the victory. When it is remembered that these were the same battalions which had lost so terribly at Neuve Chapelle just two months before, one can but marvel at the iron nerve which, enabled them once again to endure so searching a test.
It has been stated that the Kensingtons were given a separate mission of their own in the capture and bourg defence of a mine-crater upon the left of the British line. They actually carried not only the crater, but a considerable section of the hostile trenches, penetrating at one time as deep as the third line; but reinforcements could not reach them, their flanks were bare, and they were at last forced to retire. “It was bitter and damnable!” cries one of them out of his full heart. It was with the greatest difficulty that the remains of the gallant band were able to make their way back again to the British line of trenches. Nine officers were killed, 4 wounded, and 420 men were hit out of about 700 who went into action.
Such was the attack and bloody repulse which began the Battle of Richebourg. At the same hour the Indians and the First Corps had advanced upon the German lines to the north of Givenchy with the same undaunted courage, the same heavy losses, and the same barren result. The events of May 9 will always stand in military history as among the most honourable, but also the most arduous, of the many hard experiences of the British soldiers in France.
In the case of the Indians, the attack was checked early, and could make no headway against the terribly arduous conditions. Their advance was upon the right of that already described of the Fourth Corps. Farther still to the right or to the south in the region of Richebourg l’Avoué was the front of the First Division, which was fated to be even more heavily punished than the Eighth had been in the north. In this case also there was a prelude of forty minutes’ concentrated fire a period which, as the result L showed, was entirely inadequate to neutralise the many obstacles with which the stormers were faced.
During the night, the sappers had bridged the ditches between the front trenches and the supports, and had also crept out and thrown bridges over the ditches between the two lines. The 2nd Brigade (Thesiger), consisting of the 1st Northamptons, 2nd and 5th Sussex, 2nd Rifles, 1st North Lancashires, and 9th Liverpools, attacked upon the right indeed, they formed at that moment the extreme right of the whole British Army, save for the Forty-seventh London Division to the south. The weather was bright and clear, but the effect of the bombardment was to raise such a cloud of dust that two men from each platoon in the front line were able to carry forward a light bridge with which they gained a line about eighty yards from the enemy’s parapet. The instant that the guns ceased, the infantry dashed forward, but were met by a withering fire. The 1st Northamptons and 2nd Sussex were in the lead, and the ground between the armies was littered with their bodies. In a second wave came the 2nd Rifles and the 5th Sussex, but human valour could do nothing against the pelting sleet of lead. The wire had been very imperfectly cut, and it was impossible to get through. The survivors fell back into the front trenches, while their comrades lay in lines and heaps upon the bullet-swept plain. The 5th Sussex Territorials had their baptism of fire, the first and last for many, and carried themselves like men. A line of German machine-guns was posted in a very close position almost at right angles to the advance, and it was these which inflicted the heaviest losses. Hardly a single man got as far as the German parapet. At 6:20 the assault was a definite failure.
On the left, the 3rd Brigade had kept pace with the 2nd, and had shared its trials and its losses. The van of the charging brigade was formed by the 2nd Munsters and the 2nd Welsh. The 1st Gloucesters, 1st South Wales Borderers, and 4th Welsh Fusiliers were in close support. Their attack was on the German line at the Rue des Bois,
The losses of the 2nd Brigade were 70 officers and 1793 men, which might have been cited as possibly the highest number incurred in the same length of time up to that time, had it not been for the terrible figures of the 25th Brigade upon the same fatal day. The other two brigades of the Division were hard hit, the total losses of the Division amounting to nearly 5000 men. If the loss of the Indian Corps be included, the number of casualties in this assault cannot have been less than from 12,000 to 13,000 men; while the losses to the enemy inflicted by the artillery could not possibly have approximated to this figure, nor had any advantage been obtained.