Oxford Handbook of Midwifery (120 page)
Read Oxford Handbook of Midwifery Online
Authors: Janet Medforth,Sue Battersby,Maggie Evans,Beverley Marsh,Angela Walker

- It needs to be carefully disposed of.
- For women unable to touch their genital area with comfort it is not a good method to recommend.
Points to remember
- In the first few weeks after birth, intercourse may be uncomfortable or sore. Advise her to use an additional lubricant, if necessary.
- Advise the woman about the availability of emergency contraception, in case of failure to use or failure in use.
CHAPTER 22
Contraception558
- If a mother is not breastfeeding or is post-abortion, her risk of pregnancy, even in the first menstrual cycle, is real. We have all seen the woman who comes for her postnatal examination and is pregnant again!
- For the mother who is fully breastfeeding, day and night, the risk of pregnancy is minimal. If this woman chooses to use a female condom, although it is very well lubricated, she may need additional lubrication because of the very low oestrogen levels while breastfeeding.
- If one or more partners are sensitive or allergic to latex, this is a useful alternative.
- She may use additional spermicides to increase efficacy of the condom.
- Emphasize that the condom is a ‘once only’ use and should never be re-used.
- In the UK all contraception is free of charge and the midwife can offer the woman a supply of female condoms. Make sure you know where the local contraception and sexual health clinics are located, to be able to advise her on further supplies.
- Remind her to check that the condom she is purchasing has the nationally agreed quality mark, e.g. the British Kite mark or the European Community CE mark.

This page intentionally left blank
CHAPTER 22
Contraception560
Diaphragms and cervical caps
Diaphragms (Fig. 22.7) and cervical caps fit into the vagina and cover the cervix, providing a barrier to sperm, thus preventing fertilization.
Fitting and teaching of the method must be done by a doctor, nurse, or midwife trained and competent to do so. Accurate fitting is essential to their success in use.
How are they used?
- Diaphragms, in particular, are simple to use, once taught by a doctor or nurse experienced in fitting and teaching use of this method.
- The diaphragm comes in sizes from 55mm to 100mm and careful measuring and fitting is important.
- It can be inserted well ahead of intercourse and need not affect spontaneity.
- If more than 3h have elapsed since spermicide was applied, it must be reapplied before intercourse, usually in the form of a spermicidal pessary.
- The spermicide should be reapplied before repeated acts of intercourse.
- 2
It must be left in place for at least 6h after intercourse
. Efficacy
Efficacy - When used carefully and consistently, with spermicide, they have a 92–96% success rate.
- Typically the efficacy rate is 82–90%, with a spermicide.
- The failure rate depends on how effectively the woman uses the diaphragm or cervical cap.
- Age is relevant, as the woman aged 25 is generally more fertile than a woman aged 40+.
Disadvantages
- Requires motivation and needs to be used carefully and consistently.
- Needs to be used with a spermicide cream or gel for maximum effectiveness. Some women find the additional spermicide messy and unacceptable.
- No protection against HIV.
- May increase the incidence of cystitis and urinary tract infection (particularly if the diaphragm is too big).
- The woman must be comfortable with handling and exploring her body.
- Psychosexual problems may become apparent during discussion and teaching diaphragm or cervical cap fitting.
Advantages
- There is little reduction in sexual sensitivity.
- It may give some protection against cervical cancer and sexually transmitted diseases, if the cervix is covered.
- No hormones to take.
- It is under the control of the woman.
Contraindications
- Poor vaginal muscle tone, bladder, or uterine prolapse
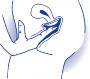
Ensure the diaphragm completely covers the cervix
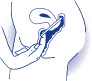
To remove the diaphragm place the forefinger over the power edge and gently pull downwards
Fig. 22.7
The diaphragm.
Copyright © fpa 2008 and reproduced by permission of the publisher.
- If a mother is not breastfeeding or is post-abortion, her risk of pregnancy, even in the first menstrual cycle, is real. We have all seen the woman who comes for her postnatal examination and is pregnant again!
- Allergy to spermicide or latex
- Undiagnosed genital tract bleeding
- Congenital abnormality, such as two cervices or septal wall defects in the vagina
- Current vaginal, cervical, or pelvic infection
- Recurrent urinary tract infections
- Past history of toxic shock syndrome
- Women unable to touch their genital area.
Side-effects
- Urinary tract infection
- Vaginal irritation
- Toxic shock syndrome if left in longer than 30h.
Points to remember
- 2 After any pregnancy the diaphragm or cap should be refitted. This is particularly important after a full-term pregnancy.
- Fitting should be delayed until at least 6 weeks after birth, to allow for return of pelvic tone.
- Advise the woman to have a diaphragm or cap properly fitted by a competent nurse, doctor, or midwife.
- If her weight varies by more than 7lb (3kg) the fitting should be professionally reassessed.
- The diaphragm must be checked regularly for deterioration or holes.
- A new diaphragm should be fitted following any episode of treated vaginal infection.
- Only water-based lubricants should be used, as any other preparations damage the latex rubber.
DIAPHRAGMS AND CERVICAL CAPS
561
CHAPTER 22
Contraception562
Fertility awareness (natural family planning)
- Fertility awareness methods are natural, requiring no medical intervention, but do require competent education in their use.
- Natural methods of family planning are widely and successfully used, particularly in certain religious groups.
- Natural fertility awareness methods involve observation of female body changes within the woman’s menstrual cycle, in order to detect ovulation, either to use as contraception or to achieve pregnancy in the fertile period.
- Many women/couples now want to utilize non-hormonal methods of contraception.
- There are four main methods of natural family planning and fertility awareness:
- Temperature method
- Calendar method
- Cervical mucus method (Billing’s method)
- A combination of the above, known as the symptothermal method, which is the most effective and preferable method (see Fig. 22.8).
 After pregnancy
After pregnancy2 Because of the hormonal changes in pregnancy, it is important to remind the woman that this method should not be relied on until she has had at least three normal periods after abortion or birth. This is to ensure that her natural hormonal levels are back to normal.
Changing from a hormonal method of contraception
2 As above, she should wait until at least three normal periods after dis- continuing the hormonal method.
Breastfeeding
- Temperature method
- 2 This method cannot be used while a mother is breastfeeding, because of altered hormone levels (for further details, b see Lactational amenorrhoea method, p. 528).
- She should wait until she has ceased breastfeeding and had at least three normal periods.
- She may need additional contraception in the intervening period.
Efficacy
- This depends on consistency and conscientiousness of method use.
- The efficacy rate varies from 80–90%.
Disadvantages
- Cannot be used immediately after pregnancy.
- Requires motivation and conscientiousness in use.
- Requires observation and recording of daily body changes.
- Requires specialist teaching.
- Takes time to learn (typically 3–6 months).
FERTILITY AWARENESS (NATURAL FAMILY PLANNING)
563
- Fertility awareness methods are natural, requiring no medical intervention, but do require competent education in their use.
Other books
Unbound by Sara Humphreys
Fast and Loose by Fern Michaels
The Endless Forest by Sara Donati
The Path of Silence by Edita A. Petrick
A Taste Of Sin by Jami Alden
The Troika Dolls by Miranda Darling
The Grandmothers by Doris Lessing
No Year of the Cat by Mary Dodson Wade
The Steps by Rachel Cohn
Still thicker than water by Takerra, Allen