Ross & Wilson Anatomy and Physiology in Health and Illness (203 page)
Read Ross & Wilson Anatomy and Physiology in Health and Illness Online
Authors: Anne Waugh,Allison Grant
Tags: #Medical, #Nursing, #General, #Anatomy

Learning outcomes
After studying this section, you should be able to:
describe the main structures of the external genitalia
explain the structure and function of the vagina
describe the location, structure and function of the uterus and the uterine tubes
discuss the process of ovulation and the hormones that control it
outline the changes that occur in the female at puberty, including the physiology of menstruation
describe the structure and function of the female breast.
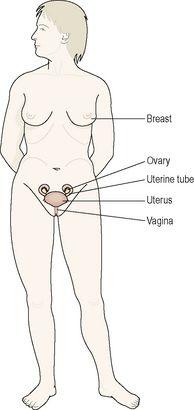
The female reproductive organs, or genitalia, include both external and internal organs (
Fig. 18.1
).
Figure 18.1
The female reproductive organs.
Faint lines indicate the positions of the lower ribs and the pelvis.
External genitalia (vulva)
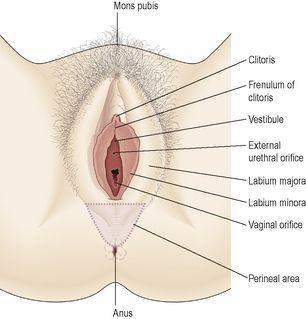
The external genitalia (
Fig. 18.2
) are known collectively as the vulva, and consist of the labia majora and labia minora, the clitoris, the vaginal orifice, the vestibule, the hymen and the vestibular glands (Bartholin’s glands).
Figure 18.2
The external genitalia of the female.
Labia majora
These are the two large folds forming the boundary of the vulva. They are composed of skin, fibrous tissue and fat and contain large numbers of sebaceous glands. Anteriorly the folds join in front of the symphysis pubis, and posteriorly they merge with the skin of the perineum. At puberty, hair grows on the mons pubis and on the lateral surfaces of the labia majora.
Labia minora
These are two smaller folds of skin between the labia majora, containing numerous sebaceous glands.
The cleft between the labia minora is the
vestibule
. The vagina, urethra and ducts of the greater vestibular glands open into the vestibule.
Clitoris
The clitoris corresponds to the penis in the male and contains sensory nerve endings and erectile tissue, but it has no reproductive significance.
Hymen
The hymen is a thin layer of mucous membrane that partially occludes the opening of the vagina. It is normally incomplete to allow for passage of menstrual flow.
Vestibular glands