The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions (1660 page)
Read The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions Online
Authors: John Bowker

BOOK: The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions
9.3Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
Nara Buddhism
.
.
The place and period (709–84) in which Buddhism was enduringly introduced into Japan. The prince-regent Sh
 toku Taishi (574–622) became a devout follower of Buddhism, accepting Korean emissaries and sending to China for further support and instruction. In 604 he promulgated the ‘Seventeen Article Constitution’ which included (Art. 2) the instruction to reverence the
toku Taishi (574–622) became a devout follower of Buddhism, accepting Korean emissaries and sending to China for further support and instruction. In 604 he promulgated the ‘Seventeen Article Constitution’ which included (Art. 2) the instruction to reverence the
Three Jewels
. Most of the emperors and empresses in the 8th cent. were Buddhist, and the court patronage led to a profusion of sects and building, especially in the capital, Nara, founded by the emperor
Sh
 mu
mu
(701–56) in 710. The proliferation of sects was such that an alternative title for the period is that of ‘The Six Sects’ (Nanto Rokushu), of which the most important and enduring were
Sanron
, Hoss
 , and
, and
Kegon
, the others being
Ritsu
, Kusha, and Jojitsu, all
H
 nay
nay
 na
na
-based. The Buddhism which flourished as a state religion was concerned with the ‘nation-protecting’ qualities of s
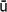 tras,
tras,
bodhisattvas
, and other guardians. The emperor Sh
 mu gave particular impetus to the building of many temples, particularly in Nara. He founded Temples of Golden Light and of the Four
mu gave particular impetus to the building of many temples, particularly in Nara. He founded Temples of Golden Light and of the Four
Devas
in all the provinces, and he planned and built the
daibutsu
(large image of Birushan/
Vairocana
) in T
 dai-ji, so that the power of Birushan would emanate to the local temples from the centre. The Great Buddha Hall, said to be the largest wooden structure in the world, was restored in 1980. Other important temple complexes are J
dai-ji, so that the power of Birushan would emanate to the local temples from the centre. The Great Buddha Hall, said to be the largest wooden structure in the world, was restored in 1980. Other important temple complexes are J
 ruri-ji (
ruri-ji (
Shingon
Ritsu), founded 1047, with
Amida
images from the Heian period; K
 fuku-ji, founded
fuku-ji, founded
c.
670 (Hoss
 ); Shinyakushi-ji (Shingon Ritsu), founded 745; T
); Shinyakushi-ji (Shingon Ritsu), founded 745; T
 sh
sh

 toku Taishi (574–622) became a devout follower of Buddhism, accepting Korean emissaries and sending to China for further support and instruction. In 604 he promulgated the ‘Seventeen Article Constitution’ which included (Art. 2) the instruction to reverence the
toku Taishi (574–622) became a devout follower of Buddhism, accepting Korean emissaries and sending to China for further support and instruction. In 604 he promulgated the ‘Seventeen Article Constitution’ which included (Art. 2) the instruction to reverence theThree Jewels
. Most of the emperors and empresses in the 8th cent. were Buddhist, and the court patronage led to a profusion of sects and building, especially in the capital, Nara, founded by the emperor
Sh
 mu
mu(701–56) in 710. The proliferation of sects was such that an alternative title for the period is that of ‘The Six Sects’ (Nanto Rokushu), of which the most important and enduring were
Sanron
, Hoss
 , and
, andKegon
, the others being
Ritsu
, Kusha, and Jojitsu, all
H
 nay
nay na
na-based. The Buddhism which flourished as a state religion was concerned with the ‘nation-protecting’ qualities of s
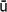 tras,
tras,bodhisattvas
, and other guardians. The emperor Sh
 mu gave particular impetus to the building of many temples, particularly in Nara. He founded Temples of Golden Light and of the Four
mu gave particular impetus to the building of many temples, particularly in Nara. He founded Temples of Golden Light and of the FourDevas
in all the provinces, and he planned and built the
daibutsu
(large image of Birushan/
Vairocana
) in T
 dai-ji, so that the power of Birushan would emanate to the local temples from the centre. The Great Buddha Hall, said to be the largest wooden structure in the world, was restored in 1980. Other important temple complexes are J
dai-ji, so that the power of Birushan would emanate to the local temples from the centre. The Great Buddha Hall, said to be the largest wooden structure in the world, was restored in 1980. Other important temple complexes are J ruri-ji (
ruri-ji (Shingon
Ritsu), founded 1047, with
Amida
images from the Heian period; K
 fuku-ji, founded
fuku-ji, foundedc.
670 (Hoss
 ); Shinyakushi-ji (Shingon Ritsu), founded 745; T
); Shinyakushi-ji (Shingon Ritsu), founded 745; T sh
sh
Other books
The Lost Boy and The Gardener's Daughter by Todd, Ian
The Two of Swords: Part 10 by K. J. Parker
The Salisbury Manuscript by Philip Gooden
Dear Lumpy by Mortimer, Louise
Sealed with a Diss by Lisi Harrison
Zombified (Episode 3): Garden Harbor by Spirito, Matt Di
Sun Kissed (Camp Boyfriend) by Joanne Rock
High Heat by Tim Wendel
Argus: Accepting the Challenge by Jana Leigh
Alien Terrain by Iris Astres