The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions (201 page)
Read The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions Online
Authors: John Bowker

BOOK: The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions
13.41Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
Anicca
(P
 li, ‘impermanent’, ‘not enduring’)
li, ‘impermanent’, ‘not enduring’)
Anitya
(Skt.), One of the
Three Marks of Existence
in Buddhism. The teaching of the impermanence or transitoriness of all things is central to the whole of Buddhist philosophy and practice. It involves the affirmation, as a truth statement, that all phenomena, both mental and physical, are without exception impermanent.
There are various ways in which the truth of the universality of impermanence is spoken of. Figuratively, the action of time is compared to the wheel of a moving chariot (which only touches the ground at one point at a time), an ever-flowing mountain stream, a bubble, a mirage, the sound of a bell. Analytically, ‘impermanence’, is to be observed in the fact that all things exist in dependence on something else, arise out of and become something else: no thing exists in isolation, no thing possesses stability. It is precisely in this respect that
nirv
 na
na
is to be understood as the direct antithesis of anicca, that is, as comprising duration, stability, and permanence, and why it is regarded as worthy of our aspiration, unlike the things of this world. The teaching on anicca links up with the Buddhist doctrine of ‘dependent origination’ (
paticca-samupp
 da
da
) which states that ‘all things have a beginning’ and that ‘all things with a beginning must have an end’; the doctrine of anicca draws attention to the fact of their demise. The paramount importance of anicca in Buddhist teaching is spotlighted in the Buddha's last words, ‘decay is inherent in all things’.
In consequence of all this, Buddhism teaches the practice of
anicc
 nupassan
nupassan
 (‘contemplation of impermanence’; cf.
(‘contemplation of impermanence’; cf.
VIPASSAN
 ) as the way of realizing the truth of impermanence. The actual process of contemplation involves ‘watching’ the rise or appearance of a given datum, verifying its ‘dependent’ or ‘caused’ origin; then, by the same token, ‘watching’ its subsidence or disappearance and verifying its transient characteristic.
) as the way of realizing the truth of impermanence. The actual process of contemplation involves ‘watching’ the rise or appearance of a given datum, verifying its ‘dependent’ or ‘caused’ origin; then, by the same token, ‘watching’ its subsidence or disappearance and verifying its transient characteristic.
Acceding intellectually to the truth of impermanence is termed in Buddhism the acquisition of ‘right view’ (
samm
 -di
-di
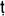
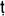 hi
hi
; see
A
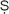
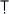 ANGIKA-M
ANGIKA-M
 RGA
RGA
) and is synonymous with entry on to the path to enlightenment.
 li, ‘impermanent’, ‘not enduring’)
li, ‘impermanent’, ‘not enduring’)Anitya
(Skt.), One of the
Three Marks of Existence
in Buddhism. The teaching of the impermanence or transitoriness of all things is central to the whole of Buddhist philosophy and practice. It involves the affirmation, as a truth statement, that all phenomena, both mental and physical, are without exception impermanent.
There are various ways in which the truth of the universality of impermanence is spoken of. Figuratively, the action of time is compared to the wheel of a moving chariot (which only touches the ground at one point at a time), an ever-flowing mountain stream, a bubble, a mirage, the sound of a bell. Analytically, ‘impermanence’, is to be observed in the fact that all things exist in dependence on something else, arise out of and become something else: no thing exists in isolation, no thing possesses stability. It is precisely in this respect that
nirv
 na
nais to be understood as the direct antithesis of anicca, that is, as comprising duration, stability, and permanence, and why it is regarded as worthy of our aspiration, unlike the things of this world. The teaching on anicca links up with the Buddhist doctrine of ‘dependent origination’ (
paticca-samupp
 da
da) which states that ‘all things have a beginning’ and that ‘all things with a beginning must have an end’; the doctrine of anicca draws attention to the fact of their demise. The paramount importance of anicca in Buddhist teaching is spotlighted in the Buddha's last words, ‘decay is inherent in all things’.
In consequence of all this, Buddhism teaches the practice of
anicc
 nupassan
nupassan (‘contemplation of impermanence’; cf.
(‘contemplation of impermanence’; cf.VIPASSAN
 ) as the way of realizing the truth of impermanence. The actual process of contemplation involves ‘watching’ the rise or appearance of a given datum, verifying its ‘dependent’ or ‘caused’ origin; then, by the same token, ‘watching’ its subsidence or disappearance and verifying its transient characteristic.
) as the way of realizing the truth of impermanence. The actual process of contemplation involves ‘watching’ the rise or appearance of a given datum, verifying its ‘dependent’ or ‘caused’ origin; then, by the same token, ‘watching’ its subsidence or disappearance and verifying its transient characteristic.Acceding intellectually to the truth of impermanence is termed in Buddhism the acquisition of ‘right view’ (
samm
 -di
-di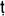
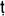 hi
hi; see
A
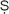
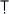 ANGIKA-M
ANGIKA-M RGA
RGA) and is synonymous with entry on to the path to enlightenment.
Other books
Fatherland by Robert Harris
Twisted Justice by Patricia Gussin
Saving Margaret by Krystal Shannan
Fractured Earth Saga 1: Apocalypse Orphan by Tim Allen
Hospital by Julie Salamon
Playing for Pizza by John Grisham
Returning to Earth by Jim Harrison
Wildlight by Robyn Mundy
Out of the Deep by Gloria Skurzynski

