The Interstellar Age
Read The Interstellar Age Online
Authors: Jim Bell


ALSO BY JIM BELL
Postcards from Mars
Mars 3-D
Moon 3-D
The Space Book
Published by the Penguin Group
Penguin Group (USA) LLC
375 Hudson Street
New York, New York 10014

USA | Canada | UK | Ireland | Australia | New Zealand | India | South Africa | China
A Penguin Random House Company
Copyright © 2015 by Jim Bell
Penguin supports copyright. Copyright fuels creativity, encourages diverse voices, promotes free speech, and creates a vibrant culture. Thank you for buying an authorized edition of this book and for complying with copyright laws by not reproducing, scanning, or distributing any part of it in any form without permission. You are supporting writers and allowing Penguin to continue to publish books for every reader.
DUTTON—EST. 1852 (Stylized) and DUTTON are registered trademarks of Penguin Group (USA) LLC.
LIBRARY OF CONGRESS CATALOGING-IN-PUBLICATION DATA
Bell, Jim, 1965–
The interstellar age : inside the forty-year Voyager mission / Jim Bell.
pages cm
ISBN 978-0-698-18615-6
1. Planets—Exploration. 2. Outer space—Exploration. 3. Voyager Project. I. Title.
QB601.B45 2015
919.9'204—dc23
2014031706
While the author has made every effort to provide accurate telephone numbers, Internet addresses, and other contact information at the time of publication, neither the publisher nor the author assumes any responsibility for errors or for changes that occur after publication. Further, the publisher does not have any control over and does not assume any responsibility for author or third-party websites or their content.
Version_1
To the men and women of
Voyager,
and the generations that they have inspired
Contents
Also by Jim Bell
Title Page
Copyright
Dedication
Prelude: Outbound
1. Voyagers
2. Gravity Assist
3. Message in a Bottle
4. New Worlds among the King’s Court
5. Drama within the Rings
6. Bull’s-Eye at a Tilted World
7. Last of the Ice Giants
8. Five Billion People per Pixel
9. The Edge of Interstellar Space
10. Other Stars, Other Planets, Other Life
Postscript: NewSpace
Photographs
Notes and Further Reading
Acknowledgments
Index
Prelude: Outbound
I believe our future depends, powerfully, on how well we understand this Cosmos in which we float like a mote of dust in the morning sky. We’re about to begin a journey through the Cosmos . . . it’s a story about us . . . how the Cosmos has shaped our evolution and our culture, and what our fate may be.
—Carl Sagan
(
Cosmos: A Personal Journey
)
P
HYSICS TELLS US
that all things attract each other gravitationally, from pulsars to planets to petunias, even if those forces are sometimes too small to notice in everyday life. But if you look closely at the trajectories that your life has taken, you may notice the results of similar gravitational effects from the people you have known. Sometimes people around us cause massive swings in direction and speed that can propel us on toward new and undiscovered territory and experiences. That’s what happened with me and the space-exploration mission known as
Voyager
.
The trajectory of my life has been guided by the slow, gentle, persistent gravitational pull of two elegant robotic spacecraft and
the teams of people—scientists, engineers, mentors, students—who made their missions of exploration so marvelously compelling. Taking advantage of a rare celestial alignment of the planets, those two robots,
Voyager 1
and
Voyager 2
, gave us all our first detailed, high-resolution, glorious views of the solar system beyond Mars, revealing the giant planets Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune, and their panoply of rings and moons, in all their awesome wonder—not just for scientists, but also for poets, musicians, painters, novelists, moviemakers, historians, and even kids.
I happened to have been born at a time that placed me in college and graduate school right when the fruits of that fortuitous celestial alignment were ripening. By a random turn of a corner in a building, while walking back from class, I spotted a flyer from a professor who was looking for student research help. I soon found myself
involved
in the missions of these extraordinary projections of human technology—something I had dreamed of since I could barely read. I felt as if I had been cast out into deep space myself, seeing my life, and my world, from a completely new perspective. In one seemingly chance Forrest Gump–like encounter after another, the arc of my life has been shaped by the
Voyager
missions, and even to this day I find myself drawn to their power to lift the human spirit. Just think of these sophisticated creations—mere machines, yet projections of ourselves—launched into my hero Carl Sagan’s “shallow depths of the cosmic ocean,” representing the integrated abilities, hopes, dreams, and fears of the more than 100 billion people who have lived on planet Earth and who, like me, have wondered, “Are we alone?” “What else is out there?” “What is our destiny?”
These Voyagers—and by that I mean the people as well as the machines—have taken us all on a tour of the Greatest Hits of the
Solar System, and we have all been privileged passengers carried along for the ride. Along the way, I went from a starry-eyed kid interested in astronomy and planetary science to a student learning the ropes from some of the greatest masters in the field, to—now—a practitioner of the art myself, with students of my own. It has been an adventure filled with astounding beauty, discovering new worlds so exotic that their alien landscapes were entirely unanticipated, facing unprecedented challenges, meeting and then saying good-bye to new friends and colleagues. . . .
And now the
Voyagers
are leaving the protective bubble of our sun and crossing over into the uncharted territory between the stars. They—and we, through them—are now interstellar travelers. Via their technology, their discoveries, and the messages that they are delivering to the galaxy on our behalf, we have all entered the Interstellar Age. This may be the ultimate legacy of the men and women and machines of
Voyager.
As we learn and grow as a species, as we begin to grasp the fragility of our existence and the fleeting nature of habitable environments in our solar system, we must adapt and move on. In the long run—the
very
long run—we will have to leave our sun’s cradle and move out into the stars. The Interstellar Age is the inevitable future of humankind, and the
Voyagers
are our first baby steps along that path.
I want to share that story with you here and convey, I hope, how special it has been to be witness to what historians of the future will no doubt regard as some of the most incredible voyages of exploration ever
attempted.
Part One
ALIGNMENT

1
Voyagers
I
GAZED IN
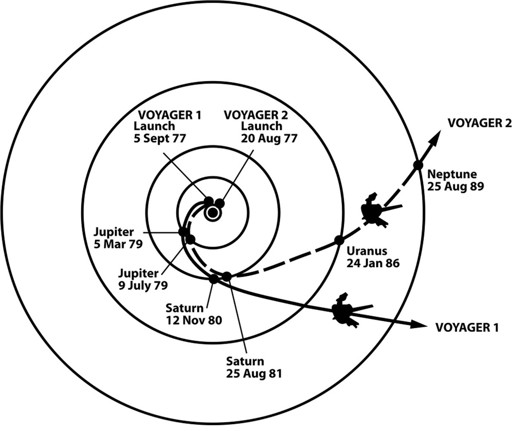
wonder at the graceful and swirling azure clouds of Neptune. I had impulsively boarded the spacecraft in 1977, at the age of twelve, seeking a place where the gravity of my world would be but a distant memory. Word of the launch came on the evening news. “A Grand Tour of the Solar System!” the announcer proclaimed. Two launches would carry our band of travelers destined for Jupiter and Saturn, and if all went well, we would forge on, perhaps past Uranus and Neptune—worlds as yet unexplored. The thought of running away from home to explore some distant land tugged at me, as it did for many preteens. In the world of my small Rhode Island town, even traveling to another area code may as well have been like traveling to Mars. Of course, it could only ever be a dream:
traveling faster than any rocket had ever gone, taking two years to Jupiter, three years to Saturn, Uranus by the mid-’80s, Neptune by my twenty-fourth birthday . . .
It sounds like science fiction, but this is essentially a true story. The spaceships are called
Voyager 1
and
Voyager 2
, and they really did launch in 1977. While the
Voyagers
don’t carry humans on board, they do carry our eyes and ears, our most sophisticated cognitive intelligence, our science and art and dreams. In 1977 they brought me out of that sheltered world of childhood and into a fantastic new world of learning, culture, and Big Science, first as a college student at Caltech in Pasadena, then as a graduate student in Hawaii.
Voyager
’s story of exploration parallels my own. Indeed, the missions have touched countless lives and careers in space science and engineering—so many of the people I know and have worked with over the decades feel as if the
Voyagers
propelled their lives
.
The “Grand Tour” announced that day in 1977 would take advantage of a once-every-176-year planetary alignment that provided an opportunity to send a single spacecraft past
all four
giant outer solar system planets, using the gravity of one to slingshot the mission on a path to the next, bouncing it from one remarkable world to another, and then eventually completely out of our solar system. The last time such an alignment occurred, back in the eighteenth century, the frontier of exploration was defined by European wooden sailing ships.