Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis (1241 page)
Authors: Mary A. Williamson Mt(ascp) Phd,L. Michael Snyder Md

BOOK: Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis
12.06Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
Because of widespread dietary use of iodine in the United States, RAIU should not be used to evaluate euthyroid state.
Increased by withdrawal rebound (thyroid hormones, propylthiouracil), increased iodine excretion (e.g., diuretics, nephrotic syndrome, chronic diarrhea), decreased iodine intake (salt restriction, iodine deficiency).
THYROID-STIMULATING HORMONE (TSH)
Definition
This glycoprotein hormone of 28–30 kDa is composed of alpha and beta subunits. It is secreted by the anterior pituitary. TSH controls the biosynthesis and release of thyroid hormones T
4
and T
3
.

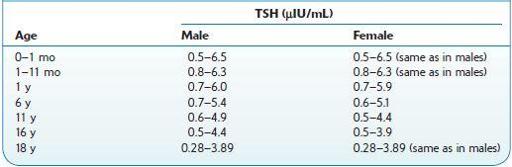
Normal range:
0.5–6.3 μIU/mL, depending on age and sex (Table 16.78).
TABLE 16–78. Normal Ranges of TSH According to Age and Sex
Use
Sensitive measure of thyroid function. First line of test for suspected thyroid disorders
Assessing true metabolic status
Screening for euthyroidism
Normal level in stable ambulatory patient not on interfering drugs excludes thyroid hormone excess or deficiency.
TSH is recommended as the initial test rather than T
4
.
Screening is not recommended for asymptomatic persons without suspicion of thyroid disease or for hospital patients with acute medical or psychiatric illness.
Other books
A Whisper to the Living by Ruth Hamilton
The case of the missing books by Ian Sansom
Jessica (Tucked In 2) by Kuhn, N
Redwood Bend by Robyn Carr
Harrigan and Grace - 01 - Blood Redemption by Alex Palmer
Dead Centre by Andy McNab
Erotic Deception by Karen Cote'
The Angel's Game by Carlos Ruiz Zafon
The Story by Judith Miller
Unforgivable by Tina Wainscott