Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis (1328 page)
Authors: Mary A. Williamson Mt(ascp) Phd,L. Michael Snyder Md

BOOK: Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis
13.75Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
A sensitive serum serology screening test for the detection of IgG and/or IgM antibodies to
Borrelia burgdorferi
.
Use
This test is used if Lyme disease is suspected in at-risk patients. Testing is not necessary if a patient presents with a tick bite and erythema migrans.
Interpretation
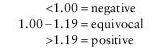
Note
: Current CDC recommendations state that equivocal and positive results should be confirmed with Western blot prior to reporting screen results. If testing is negative, consider other tick-borne diseases (i.e.,
Babesia
,
Ehrlichia
).
Limitations
Should not be used to screen general population. False-negative results can occur if the patient is tested too early; repeat testing in 2–4 weeks. The IgG antibody response is usually not detectable until 4–6 weeks after infection; the IgM antibody response usually not detected during the first 2 weeks of infection, peaking 3–6 weeks following infection. False-positive results may occur from other spirochetal diseases, autoimmune diseases, or other infections (EBV, HIV, syphilis, infectious mononucleosis, etc.). IgG antibodies can be detected as early as 2 weeks, and both IgM and IgG antibodies can remain detectable for years. Diagnosis depends on clinical features, combined with available laboratory tests.
Suggested Reading
FDA Public Health Advisory: Assays for Antibodies to Borrelia burgdorferi; Limitations, Use, and Interpretation for Supporting a Clinical Diagnosis of Lyme Disease. July 7, 1997.
http://www.fda.gov/MedicalDevices/Safety/AlertsandNotices/PublicHealthNotifications/UCM062429
BORRELIA BURGDORFERI
(LYME DISEASE)—WESTERN BLOT
*
Definition
The western blot assay for antibodies to
Borrelia burgdorferi
, the etiologic agent of Lyme disease, is a qualitative method of categorizing specific immuno-reactivities in serum or plasma to
B
.
burgdorferi
proteins that have been formatted according to molecular weight into discrete bands on nitrocellulose strips.

Normal range:
Negative.
Use
The western blot assay for
B
.
burgdorferi
is used as a second-tier test to characterize the specificity of an individual’s immune response to the component proteins of
B
.
burgdorferi
by identifying the presence, relative level, and pattern of reactivities to the complete set of the bacterial proteins. The assay is used routinely to provide supportive serologic evidence of infection following a more sensitive but less specific screening test (such as EIA) for general reactivity to
B
.
burgdorferi
. Both IgM and IgG reactivities to the bacterial proteins are assayed to provide information on the evolution of the immune response relative to the stage of infection (i.e., early localized, early disseminated, or late disseminated). A caveat to this use is that IgM testing is not recommended in patients with symptoms lasting greater than 1–2 months. For such patients, IgG testing alone should be performed.
Other books
1 - Interrupted Aria by Beverle Graves Myers
Mistress at a Price by Sara Craven
Unformed Landscape by Peter Stamm
Let It Shine by Alyssa Cole
The Great Scottish Devil by Kaye, Starla
Faerie Fate by Silver James
Quarterback Daddy by Linda Barrett
Miss Jane by Brad Watson
One Last Night by Bayard, Clara