Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis (394 page)
Authors: Mary A. Williamson Mt(ascp) Phd,L. Michael Snyder Md

BOOK: Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis
6.81Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
Patients with abnormal thromboxane A
2
synthesis have an aspirin-like defect.
Impaired release of arachidonic acid.
Cyclooxygenase deficiency.
Thromboxane synthase deficiency.
Disorders of platelet–vessel wall interaction (platelet adhesion defects).

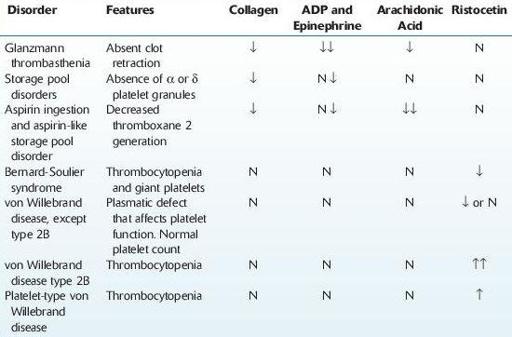
Bernard-Soulier
syndrome is an autosomal recessive disorder, caused by absence or abnormalities in the platelet receptor complex GPIb-IX-V. It presents with moderate to severe thrombocytopenia and
giant platelets
. Platelets aggregate normally with ADP, epinephrine, collagen, and arachidonic acid but show delayed aggregation with thrombin and no response to ristocetin (see Table
9-4
).

Platelet-type von Willebrand disease
autosomal dominant condition associated with intermittent thrombocytopenia, normal platelet morphology, and decreased levels of high molecular weight vWF multimers. It must be distinguished from von Willebrand disease type 2B.
Disorders of platelet function related to other defects.

Quebec platelet disorder
: excessive fibrinolysis resulting from increased expression and storage of the fibrinolytic enzyme urokinase plasminogen activator in platelets. The defect results in delayed-onset bleeding after trauma or surgery.

Scott syndrome
: autosomal recessive disorder due to a defect in platelets’ membrane resulting in inability to assemble prothrombinase and intrinsic tenase complexes.
The Montreal platelet syndrome was recently documented to be a variant of type 2B von Willebrand disease.
TABLE 9–4. Abnormalities of Platelet Function
ACQUIRED THROMBOCYTOPATHIES
Other books
Rebecca Hagan Lee by A Wanted Man
Tripoli's Target (Justin Hall # 2) by Ethan Jones
Towers of Midnight by Robert Jordan and Brandon Sanderson
Moses, Man of the Mountain by Zora Neale Hurston
Love Letters from an Alpha by Anya Byrne
Right Hand Magic by Nancy A. Collins
Devil Takes His Innocent by Emma Anderson
S.O.S by Will James
Smart Moves by Stuart M. Kaminsky