Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis (951 page)
Authors: Mary A. Williamson Mt(ascp) Phd,L. Michael Snyder Md

BOOK: Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis
8.25Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
Normal range: peak glucagon concentration at 30 minutes: 100–1,500 pg/ mL.
Limitations
Arginine also stimulates insulin.
There is an exaggerated response in diabetes, chronic renal failure, and liver failure.
GLUCOSE TOLERANCE TEST, ORAL (OGTT)
Definition and Use
OGTT should be reserved principally for patients with “borderline” fasting plasma glucose levels. It is necessary for the diagnosis of impaired fasting glucose and impaired glucose tolerance. All pregnant women should be tested for gestational DM with a 50-g dose at 24–28 weeks of pregnancy; if that is abnormal, OGTT should be performed for confirmation. OGTT is the gold standard, and currently, its chief use is in the diagnosis of gestational DM (GDM).

Normal range:
see Tables 16.35 and 16.36.
TABLE 16–35. Blood Test Levels for Diagnosis of Diabetes and Prediabetes

TABLE 16–36. Screening and Diagnostic Scheme for GDM
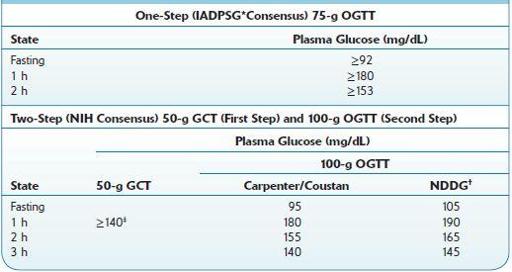
*International Association of Diabetes and Pregnancy Study Groups.
†National Diabetes Data Group.
‡American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommend 135 mg/dL for high-risk ethnic minorities with higher prevalence of GDM.
Interpretation
Criteria for the diagnosis of DM (males and nonpregnant females) (
one
of the following) (Table 16.35):
Symptoms of DM plus casual (random) plasma/serum glucose concentration ≥200 mg/dL. Casual is defined as any time of day without regard to time since the last meal.
Fasting plasma glucose (FPG) ≥126 mg/dL. Fasting is defined as no caloric intake for at least 8 hours.
Other books
The Someday Jar by Allison Morgan
Tantric Orgasm for Women by Diana Richardson
Death in Zanzibar by M. M. Kaye
Angel Boy by Bernard Ashley
Wild Rider (Bad Boy Bikers Book 2) by Lydia Pax
Body Politic by J.M. Gregson
Just Desserts : A Bed-and-breakfast Mystery by Mary Daheim
A Dead Man in Trieste by Michael Pearce
One Night with His Wife by Lynne Graham
Blind Passion by Brannan Black