Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis (957 page)
Authors: Mary A. Williamson Mt(ascp) Phd,L. Michael Snyder Md

BOOK: Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis
8.48Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
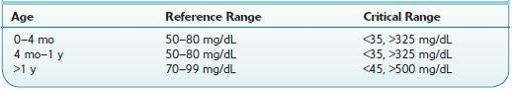
Use
Diagnosis of DM
Control of DM
Diagnosis of hypoglycemia
Other carbohydrate metabolism disorders including gestational diabetes, neonatal hypoglycemia, idiopathic hypoglycemia, and pancreatic islet cell carcinoma
Criteria for the diagnosis of DM (American Diabetes Association Expert Committee)
Four ways to diagnose diabetes are possible. Each must be confirmed on a subsequent day by any one of the four methods given above.
Symptoms of diabetes plus casual (random) plasma/serum glucose concentration ≥200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L). Casual is defined as any time of day without regard to time since the last meal.
FPG (fasting plasma glucose) ≥126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L). Fasting is defined as no caloric intake for at least 8 hours.
Two-hour PG (postload glucose) ≥200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) during an OGTT. The test should be performed using a 75-g glucose load.
HbA
1C
of >6.5%.
In the absence of unequivocal hyperglycemia with acute metabolic decompensation, these criteria should be confirmed by repeat testing on a separate day. The third measure (OGTT) is not recommended for routine clinical use.
Other books
PRINCE OF THE WIND by Charlotte Boyet-Compo
Broken Quill [2] by Joe Ducie
Faster (The University of Gatica #2) by Lexy Timms
Katie Sprinkles and Surprises by Coco Simon
Billy Mack's War by James Roy
Cover Me by Joanna Wayne Rita Herron and Mallory Kane
07 Uncorked - Chrissy McMullen Mystery by Lois Greiman
El pibe que arruinaba las fotos by Hernán Casciari
One Is Never Enough by Erica Storm