Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis (988 page)
Authors: Mary A. Williamson Mt(ascp) Phd,L. Michael Snyder Md

BOOK: Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis
7.45Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
Decreased In
Schizotypal personality disorders
Limitations
Preferred specimen is 24-hour urine, because of intermittent excretion.
Moderately elevated HVA may be caused by a variety of factors such as essential hypertension, intense anxiety, intense physical exercise, and numerous drug interactions (including some over-the-counter medications and herbal products).
Medications that may interfere include amphetamines and amphetamine-like compounds, appetite suppressants, bactrim, bromocriptine, buspirone, caffeine, chlorpromazine, clonidine, disulfiram, diuretics (in doses sufficient to deplete sodium), epinephrine, glucagon, guanethidine, histamine, hydrazine derivatives, imipramine, levodopa (
L
-dopa, Sinemet), lithium, MAO inhibitors, melatonin, methyldopa (Aldomet), morphine, nitroglycerin, nose drops, propafenone (Rythmol), radiographic agents, rauwolfia alkaloids (Reserpine), and vasodilators. The effects of some drugs on catecholamine metabolite results may not be predictable.
HUMAN CHORIONIC GONADOTROPIN (hCG)
Definition
Glycoprotein hormone, which is also known as β-hCG and chorionic gonadotropin, is produced by the placenta, with structural similarity to the pituitary hormones FSH, TSH, and LH. The hCG test is widely used to detect pregnancy. It is also used as tumor marker for choriocarcinoma and some germ cell tumors.

Normal range:
≥5.0 mIU/mL (generally indicative of pregnancy; Table 16.40).
TABLE 16–40. Representative Ranges in Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG) During Normal Pregnancy
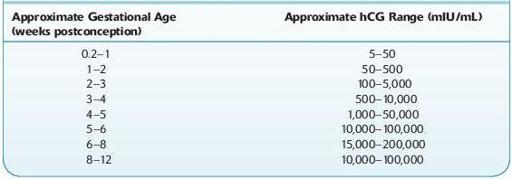
Use
Diagnosis of pregnancy
Investigation of suspected ectopic pregnancy
Monitoring in vitro fertilization patients
Other books
Sir Rowan and the Camerian Conquest by Chuck Black
Mister Pepper's Secret by Marian Hailey-Moss
Alexander and Alestria by Shan Sa
A Pirate's Heart (St. John Series) by Lora Thomas
Intertextuality and the Reading of Midrash by Daniel Boyarin
Unworthy Heart: The Donnellys, Book 1 by Dorothy F. Shaw
Til Death (Jane #5) by Samantha Warren
Phoenix Bar: A Steel Demons MC Novel by Annelise Reynolds
Tree Girl by T. A. Barron
Boy Still Missing by John Searles