Read Catastrophe 1914: Europe Goes to War Online
Authors: Max Hastings
Tags: #Ebook Club, #Chart, #Special
Catastrophe 1914: Europe Goes to War (60 page)

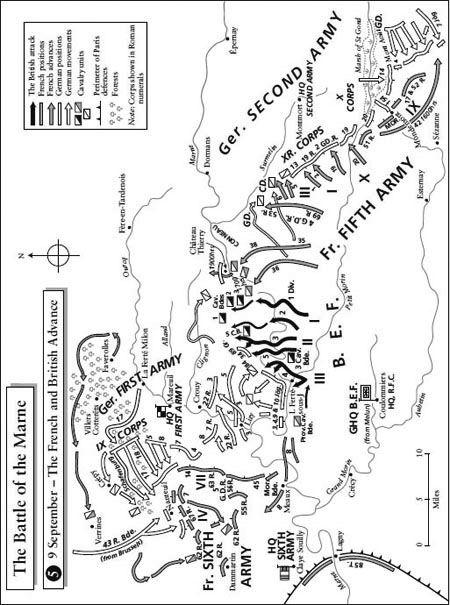
This was the moment when the fate of the Western Front hung by a thread: Castelnau was telling Joffre that he might have to abandon Nancy; Ninth Army’s right wing had crumbled; Maurice Sarrail’s Third Army was conducting a ferocious struggle to defend the Revigny Gap covering Verdun. Messages of elaborate courtesy but increasing urgency flew from Joffre to British GHQ, pleading with Sir John French to hasten the advance of the BEF. Yet at every approach to woodland, British commanders halted to reconnoitre. Their units crossed the Petit Morin almost unopposed, but by the evening of 8 September had still not reached the Marne. Maj. Tom Bridges wrote: ‘Our pursuit could not be called vigorous, but then we were still a somewhat jaded army.’ This was true enough; but what of the condition of the French, who had endured vastly worse things?
All hinged upon which army cracked. Around 1 p.m. on 8 September, the German Guards corps advancing against Foch’s right wing halted, exhausted. Their early-morning bayonet charge had been a triumph, but there were no reserves to exploit it: the three divisions which had advanced eight miles had lost a fifth of their strength. The rest of the men were gnawingly hungry, not having received rations for at least one day, and in some cases two. Most collapsed into sleep where they stopped. The weather deteriorated, bringing drizzle and mist. Fighting in the Saint-Gond marshes became confused, with some of Foch’s units attacking and some Germans falling back, while elsewhere French retreats continued. Several Ninth Army units ordered to advance refused to do so. All the combatants were in a condition of extreme exhaustion and demoralisation.
That evening, Foch presented an optimistic picture to GQG, which included direct deceits about the progress of some of his formations, and about the setbacks, withdrawals and even routs which others had experienced. The truth was that both his flanks had been squeezed, while his centre was holding only precariously. Legend has it that Foch now asserted: ‘My right is driven in, my left is falling back. Excellent. I attack with my centre.’ According to senior staff officers, these sentiments were put into the general’s mouth afterwards by Lt. André Tardieu, his voluble interpreter, who was much given to such melodramatic pronouncements. The
reality was that Ninth Army was rescued from a desperate plight less by its own efforts than by the pressure on the Germans to respond to their difficulties elsewhere.
It is a historic irony that just as Joffre and his army commanders from Lorraine to Paris were reduced to gnawing uncertainty about whether their line could hold or their offensives continue, Moltke in his turn studied the map in his Luxembourg schoolhouse and told his staff in ashen tones: ‘We know nothing! It’s terrible!’ Though the BEF was moving very slowly, Germany’s chief of staff was appalled by the spectacle of Sir John French’s divisions advancing towards the yawning gap between Bülow and Kluck, who were fighting entirely separate battles, heedless of each other’s purposes. Moltke radioed no orders to First or Second Army on 7 September – had he done so, they would probably have been ignored. Instead, all day he anguished. OHL had to endure a personal visit from Crown Prince Rupprecht, who complained bitterly about being obliged to surrender six ammunition columns to his neighbours, which he said would weaken Sixth Army’s attack on Nancy. Moltke was feeble enough to give way to Rupprecht’s demands. Then, amid the near-total breakdown of communication with his northern army commanders, the chief of staff determined to dispatch a liaison officer, Lt. Col. Richard Hentsch, to visit each headquarters in turn. This would provoke the most dramatic manifestation of delegated authority in military history.
Tappen, Moltke’s principal staff officer, often employed such emissaries, and mandated to them far-reaching powers. Hentsch was forty-five, an NCO’s son who had originally joined the Saxon rather than the Prussian army. He gained a reputation for brilliance and clear thinking, though gall-bladder troubles rendered him irascible, and he smoked heavily. No one knows precisely what orders Moltke gave Hentsch in their private conversation before his departure by motor, with a second car following in case of emergencies. But there is no doubt that the colonel was given verbal authority to use Moltke’s name to impose redeployments, if these seemed necessary. It was an extraordinary way for a general to exercise command in the midst of the greatest campaign in history, but it was what Moltke did. Hentsch set forth from the girls’ school in which the chief of staff’s headquarters were located soon after 11 a.m. on the 8th, even as Frenchmen and Germans were slaughtering each other in dreadful numbers along two hundred miles of front. Moltke then endured many hours of suspense, as he waited to hear back from his emissary.
Hentsch made a personal decision to visit all the army headquarters, rather than merely those of Bülow and Kluck. To junior officers accompanying him, he voiced some concern that Moltke had not given him orders in writing. But he thought this would prove no difficulty, and it did not. He began his travels in the Argonne. At 4 p.m. he made a first telephone call to Luxembourg, to report that in the centre of the front he found both Fourth and Fifth Armies in satisfactory condition. He reached the same conclusion about Hausen’s Third – not realising that its dashing advance of the morning had now run out of steam. Hausen still believed that he was on the brink of rolling up Foch’s line, and at 8 p.m. Moltke received a radio message to this effect.
Then, in the small hours, came another missive from Hentsch, this time dispatched from the headquarters of Bülow’s Second Army at the Château de Montmort. One of the most important radio messages of the war, it was taken to Moltke, who was still at his desk. He was writing to his wife, as he did almost daily, in tones verging upon hysteria: ‘I cannot find words to describe the crushing burden of responsibility that has weighed on my shoulders during the last few days, and still weighs upon me today. The appalling difficulties of our present situation hang before my eyes like a dark curtain through which I can see nothing. The whole world is in league against us; it would seem that every country is bent on destroying Germany, once and for all.’
The thunderbolt from Hentsch that fell upon Moltke at 2 a.m. on 9 September was a report that old Bülow was acutely alarmed about his predicament. His right wing was cracking under pressure from Franchet d’Espèrey and Foch; the French heavily outnumbered Second Army, whose effective fighting strength had fallen from 260,000 men to 154,000. Bülow had heard nothing from Kluck, but reported an eighteen-mile gap between First and Second Armies. This breach was still widening, and the British were advancing towards it. At some point in discussion with Hentsch, either Bülow or one of his staff used the word ‘
Schlacke
’ – ‘ashes’ – to describe the threatened fate of Second Army. Bülow asked the colonel to use OHL’s authority to get Kluck to close up on his flank. Hentsch, speaking in cool and measured terms, told the general this was impossible when Kluck’s army was heavily engaged, and facing in the opposite direction. Even as they were speaking, a message arrived reporting that Maud’huy had broken through Einem’s corps, and was threatening Montmirail.
Bülow was an old man in poor health, and Otto Lauenstein, his chief of staff, was also ailing – he died of heart disease in 1916. After five weeks of
vast responsibility and stress, both had had enough. Hentsch, a mere lieutenant-colonel, hereupon told Second Army’s commander that he had Moltke’s personal mandate to authorise a withdrawal by First and Second Armies. He proposed that such a movement should commence forthwith, so that Kluck and Bülow’s forces should reunite at Fismes on the Vesle river some thirty miles east, just short of Reims. Bülow appeared to assent with relief to this proposal, with its vast consequences for the battle and the war. Hentsch signalled Moltke: ‘situation at 2.Army serious, but not desperate’. Then he went to bed.
At 5 o’clock next morning, the 9th, Hentsch held a further and final discussion with Bülow’s staff, in the absence of the general himself, who had succumbed to a succession of crying fits during the night. Air reconnaissance showed the French advancing fast on Second Army’s front. Against this background, the morning meeting confirmed the previous night’s decision to retreat. Lt. Col. Hentsch had acted prudently; the course of action he adopted was almost certainly unavoidable. But the intervention of this very junior officer at a critical moment of the war would remain a focus of controversy for the ensuing century.
On leaving Bülow, the colonel set off to motor fifty miles to Kluck’s headquarters at Mareuil through the chaotic and crowded rear areas of two embattled armies and a terrorised and fleeing civilian population. His messages had already reduced Moltke to demoralisation and indeed abject defeatism: he wrote in yet another letter to his wife: ‘It goes badly. The battles east of Paris will not end in our favour … And we will certainly be made to pay for all that has been destroyed.’ At 9.02 a.m., Bülow’s troops received the order to begin a withdrawal.
Further south, however, Hausen was continuing his onslaught against Foch’s right. At dawn, German troops had seized the Château de Mondement, putting to flight a Moroccan regiment; all morning the Germans kept up a bombardment of the precarious French line, together with infantry attacks which threatened to give them command of high ground from which they could dominate the region. It was profoundly fortunate for the allies that thirty miles westward, their luck dramatically improved. Heavy rain had fallen during the night. On the morning of the 9th, French infantry advancing on Montmirail met no opposition. They found Bülow’s soldiers gone, leaving behind all the detritus of an army, together with an astounding number of empty wine bottles – broken glass carpeted the road. By a notable omission, reflecting their disarray and demoralisation, the Germans failed to destroy the Marne
bridges. This was a turning point, a decisive moment of the First World War.
That day British cavalry, followed by men of Haig’s I Corps, at last crossed the Marne, as did II Corps lower down. On 9 September gunner William Edgington wrote: ‘everyone much more cheerful now that the retirement of the Germans is assured … In the afternoon we saw most of the German army in retreat, a marvellous sight, column after column of them in countless numbers.’ Seeing the road littered with weapons and equipment, Edgington was fascinated and rather shocked that one of the abandoned German vehicles proved to be laden with women’s underclothes. The fox-hunting cavalryman Col. David Campbell contrived to lead a charge at Moncel from which he emerged beaming, despite having received a German lance thrust. ‘Best fifteen minutes of my life!’ he exclaimed happily.
Though the BEF was now advancing into a void, Sir John French ordered another halt, to allow his forces – reinforcements had arrived from England, creating a third corps alongside those of Haig and Smith-Dorrien – to realign with each other. Major Jeffreys of the Grenadiers wrote caustically: ‘It’s a precious slow pursuit and the German rear-guards seem to delay us very successfully, judging from the constant checks.’ A rumour reached Haig on the 9th that his French neighbours had suffered a ‘heavy defeat’, which intensified his caution.
Senior British officers lacked drive, will and competence, rather than courage. Indeed, like their French counterparts British commanders frequently displayed a foolish readiness to expose their persons. A staff captain watching divisional commander Aylmer Hunter-Weston standing on the street in La Ferté, heedless of bullets smacking into the wall behind him, wrote: ‘his nerve is wonderful, in fact he is much too brave for a general’. Col. Le Marchant of the East Lancashires was likewise standing in full view, having just received orders for an attack on 9 September, when a German bullet felled him. A few days later Colonels Sir Evelyn Bradford of the Seaforths and Henry Biddulph of the Rifle Brigade stood on open ground peering at a map with Capt. Jimmy Brownlow. One of them had just muttered the words ‘general advance’ when two shells burst beside them. Bradford, a former Hampshire county cricketer, was killed instantly, and Brownlow hideously wounded in the head. Biddulph found his cap blown thirty yards by the blast, but was otherwise unscathed. He was less fortunate next day, when he had to be evacuated after being shot in the ankle by a Royal Engineer who was cleaning his rifle. But these were mere battlefield incidents rather than consequences of sustained German resistance. Nobody at GHQ sought to inject urgency into British motions. The C-in-C’s overarching concern was to ensure that his command did not fall victim to any further French betrayals or German surprises.
That same morning of the 9th, Col. Hentsch had one more important call to make. He reached Kluck’s headquarters at 11.30 a.m. only after a nightmare journey on logjammed roads; at one point, Landwehr soldiers fired on his car. Everywhere nervous men told the staff group that the French had crossed the Marne and were hard on their heels. But Hentsch found Kluck and his staff confident – justly confident – that they had halted Manoury’s advance in its tracks. Now, said the general’s chief of staff, they were poised to inflict absolute defeat on the French. Manoury’s left wing was collapsing, his troops were demoralised and much reduced by losses. Yet here suddenly was Moltke’s emissary, announcing that Bülow was beaten and in retreat; that Kluck must fall back likewise, or find the BEF assaulting his rear. Hentsch emphasised the threat by describing his own journey through a chaos of stragglers, ambulance convoys, supply wagons and refugees.