How to Pass Numerical Reasoning (16 page)
Read How to Pass Numerical Reasoning Online
Authors: Heidi Smith

Adding decimals: practice drill
Set a stopwatch and aim to complete the following drill in two minutes.
Q1 | 27.97 | + | 46.83 | = |
Q2 | 162.72 | + | 87.03 | = |
Q3 | 87.003 | + | 0.04 | = |
Q4 | 34.01 | + | 152.9 | = |
Q5 | 0.001 | + | 0.002 | = |
Q6 | 9.86 | + | 5.7602 | = |
Q7 | 2.561 | + | 0.002 | = |
Q8 | –1.002 | + | 1.002 | = |
Q9 | 9.87 | + | –0.67 | = |
Q10 | –0.01 | + | –123.25 | = |
Subtracting decimals
Subtract decimals by lining up the decimal points and subtracting as normal.
Worked example
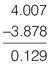
4.007 – 3.878 = ?
Tip:
When subtracting numbers, you may find it easier to count up from the number being subtracted. For example, for the subtraction 33.26 – 31.96, count up from 31.96 to 32 to give 0.04. The difference between 32 and 33.26 = 1.26, so the difference between 31.96 and 33.26 = 1.26 + 0.04 = 1.3.
Subtracting decimals: practice drill
Set a stopwatch and aim to complete the following drill in two minutes.
Q1 | 14.93 | – | 13.88 | = |
Q2 | 12.22 | – | 11.03 | = |
Q3 | 7.003 | – | 0.041 | = |
Q4 | 153.01 | – | 152.0 | = |
Q5 | 1.002 | – | 1.001 | = |
Q6 | 9.16 | – | 5.76 | = |
Q7 | 2.561 | – | 0.0027 | = |
Q8 | –5.0201 | – | 4.897 | = |
Q9 | 12.80 | – | –0.0078 | = |
Q10 | –0.01 | – | –0.001 | = |
Multiplying decimals
To multiply decimals, ignore the decimal points and multiply the numbers as if they were whole numbers. At the end of the calculation, you will reinsert the decimal point.
Worked example
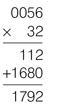
32 × 0.056
Now count up all the spaces after the decimal points of both original numbers. There are no decimal spaces to consider in 32. In 0.056 there are three spaces after the decimal point, so you must count back three spaces in your final answer and insert the decimal point.
insert the decimal point.
Answer
= 1.792
Worked example
17.6 × 2.1002 =

Line up the numbers, ignoring the decimal points
Count up the decimal places in each number. 17.6 = one decimal place; 2.1002 = four decimal places, so you must count
back (4 + 1) decimal places.
Insert the decimal point here.
Answer
= 36.96352
Multiplying decimals: practice drill
Set a stopwatch and aim to complete the following drill in two minutes.
Q1 | 1.92 | × | 12 | = |
Q2 | 12.2 | × | 11 | = |
Q3 | 17.3 | × | 0.4 | = |
Q4 | 15 | × | 1.4 | = |
Q5 | 1.2 | × | 1.2 | = |
Q6 | 19.4 | × | 5.75 | = |
Q7 | 4.51 | × | 0.271 | = |
Q8 | 77.01 | × | 0.04 | = |
Q9 | 13 | × | 0.0078 | = |
Q10 | 0.001 | × | 0.003 | = |
Dividing decimals
To divide decimals, treat all the integers in the calculation as if they were whole numbers. To do this, you will increase each integer by a multiple of 10 to produce a whole number.
Worked example
150 ÷ 7.5 = ?
Multiply both numbers by 10.
1500 ÷ 75 = 20
If only one integer is a decimal, you can increase the decimal number by a multiple of 10 and balance the calculation at the end.
Worked example
1000 ÷ 12.5 = ?
Multiply 12.5 by 10.
1000 ÷ 125 = 8
Now multiply the answer by 10 to find the result of 1000 ÷ 12.5 (12.5 is 10 times smaller than 125).
1000 ÷ 12.5 = 80
Dealing with remainders
Worked example
311.6 ÷ 15.2 = ?
Multiply both numbers by a multiple of 10.
(10 × 311.6) ÷ (10 × 15.2) = 3116 ÷ 152
If you find you have a remainder when completing the long division calculation, insert a decimal point and extra zero(s) and continue to divide until either there is no remainder or the calculation produces a recurring number for your answer.
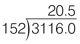
Insert decimal point and extra zeros as necessary.
Dividing decimals: practice drill
Set a stopwatch and aim to complete the following drill in two minutes.
Q1 | 30 | ÷ | 2.5 | = |
Q2 | 90 | ÷ | 4.5 | = |
Q3 | 122.5 | ÷ | 4.9 | = |
Q4 | 326.6 | ÷ | 14.2 | = |
Q5 | 144.5 | ÷ | 8.5 | = |
Q6 | 1.26 | ÷ | 0.06 | = |
Q7 | 17.49 | ÷ | 2.12 | = |
Q8 | 11.4 | ÷ | 57 | = |
Q9 | 27.9 | ÷ | 4.5 | = |
Q10 | 12.88 | ÷ | 5.6 | = |