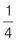How to Pass Numerical Reasoning (8 page)
Read How to Pass Numerical Reasoning Online
Authors: Heidi Smith

Dividing large numbers: practice drill
Q1 | 400 |
Q2 | 30 |
Q3 | 400 |
Q4 | 1,200 |
Q5 | 250 |
Q6 | 1,300 |
Q7 | 170,000 |
Q8 | 2,300 |
Q9 | 4,300 |
Q10 | 370 |
Multiplication and division of signed numbers: practice drill 1
Q1 | 144 |
Q2 | 144 |
Q3 | –42 |
Q4 | –351 |
Q5 | –361 |
Q6 | –9 |
Q7 | 14 |
Q8 | –45 |
Q9 | 13 |
Q10 | –18 |
Multiplication and division of signed numbers: practice drill 2
Q1 | 208 |
Q2 | –783 |
Q3 | –2,751 |
Q4 | 7,072 |
Q5 | –3,536 |
Q6 | –56 |
Q7 | 3 |
Q8 | 45 |
Q9 | –225 |
Q10 | 17 |
Averages: practice drill
Arithmetic mean: | Median: | ||
Q1 | 20 | Q6 | 4 |
Q2 | 0.2 | Q7 | –2.5 |
Q3 | 3 | Q8 | 72 |
Q4 | –5.5 | Q9 | 7.5 |
Q5 | 0.4 | Q10 | 38 |
Q11 | 23 |
Q12 | –2 |
Q13 | 1 |
Q14 |
|
Q15 | –0.1 and 0.001 |
• Terms used in this chapter
• What a fraction is
• Working with fractions
• Fraction operations
• Decimal operations
• Answers to
Chapter 2
Denominator:
The number below the line in a vulgar fraction.
Dividend:
The number to be divided.
Divisor:
The number by which another is divided.
Equivalent fractions:
Fractions with equivalent denominators and numerators.
Fraction:
A part of a whole number.
Fraction bar:
The line that separates the numerator and denominator in a vulgar fraction.
Improper fraction:
A fraction in which the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator.
Lowest common denominator:
The lowest common multiple of the denominators of several fractions.
Lowest common multiple:
The least quantity that is a multiple of two or more given values.
Mixed fractions:
A number consisting of an integer and a fraction.
Numerator:
The number above the line in a vulgar fraction.
Prime factorization:
The expression of a number as the product of its prime numbers.
Proper fraction:
A fraction less than one, with the numerator less than the denominator.
Vulgar fraction:
A fraction expressed by numerator and denominator, rather than decimally.
In
Chapter 1
, you practised operations with whole numbers. In this chapter you will practise number operations on parts of numbers. The same principles apply to decimals and fractions as to whole numbers. Additionally, there are a few extra tricks you can learn to complete these puzzles quickly and accurately.
Proper and improper fractions
A fraction is a part of a whole number, or a value expressed as one number divided by another. For example:
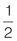 Part = 1 and whole = 2.
Part = 1 and whole = 2.
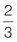 Part = 2 and whole = 3.
Part = 2 and whole = 3.
 Part = 7 and whole = 5.
Part = 7 and whole = 5.
To write a fraction, put the part over the whole and separate with a fraction bar. The number above the fraction bar is called the
numerator
and the number below the fraction bar is called the
denominator
. There are two types of fractions. A
proper fraction
is a fraction less than one, with the numerator less than the denominator. An
improper fraction
is a fraction in which the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator. For example: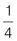 Numerator = 1 and denominator = 4 Proper fraction
Numerator = 1 and denominator = 4 Proper fraction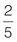 Numerator = 2 and denominator = 5 Proper fraction
Numerator = 2 and denominator = 5 Proper fraction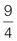 Numerator = 9 and denominator = 4 Improper fraction These terms will become useful when you start to work with fractions.
Numerator = 9 and denominator = 4 Improper fraction These terms will become useful when you start to work with fractions.
Finding the lowest common multiple
In
Chapter 1
, you practised working out the lowest common multiple. Here’s a quick refresher of this method – this is a great technique to have mastered as it will save you time when you’re working out fractions under time pressure. Review
Chapter 1
now if you need a reminder of the method to find the lowest common multiple.
Finding the lowest common denominator
To find the lowest common denominator of two or more fractions, find the lowest common multiple of all the denominators.
Worked example
What is the lowest common denominator of the following fractions?