Pro Puppet (41 page)
Authors: Jeffrey McCune James Turnbull

On both Red Hat and Ubuntu/Debian machines, you need to:
- Create a database for Foreman, and secure it with a user and password.
$ sudo mysql –p
mysql> CREATE DATABASE foreman CHARACTER SET utf8; CREATE USER 'foreman'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'password'; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON foreman.* TO 'foreman'@'localhost';
IDENTIFIED BY 'password'; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON foreman.* TO 'foreman'@'localhost'; - Edit the
database.ymlfile and specify the database details you just used.production:
database: foreman
username: foreman
password:
password
encoding: utf8
adapter: mysql Note
Note
Alternately, you can modify thedatabase.ymlfile to use the same database as your stored configuration database in Puppet. See
Chapter 6
for more details on stored configuration. - Run a Rake task to populate your database with the appropriate tables:
$ sudo RAILS_ENV=production rake db:migrate
You can also import existing data from Puppet. If you are using stored configuration with Puppet and you are sharing the database with Foreman, you can run:
$ sudo RAILS_ENV=production rake puppet:migrate:populate_hosts
If you're not using stored configuration and your Puppet master is located on the same host as Foreman, then you should run the following Rake task:
$ sudo RAILS_ENV=production rake puppet:import:hosts_and_facts
You should regularly run this task via cron to keep your nodes and facts up-to-date.
If your Puppet master is not on the same host as Foreman, you can choose between two approaches. The first uses the same import Rake task but requires that you transfer (or mount) your Puppet facts YAML output files (usually located in the/var/lib/puppet/yaml/factsdirectory) from the master to the Foreman host:
$ sudo rake RAILS_ENV=production puppet:import:hosts_and_facts dir=/path/to/yaml/files
The second approach uses Foreman's ability to receive Fact data from Puppet. Foreman comes with a script you can install onto your Puppet masters and run with cron:
$ wget --no-check-certificate https://github.com/ohadlevy/puppet-foreman/raw
 /master/foreman/files/push_facts.rb
/master/foreman/files/push_facts.rb
You will need to update this line of the script to point to the location of your Foreman installation:
url=http://foreman
 Tip
Tip
For more information on importing data to Foreman to Puppet, see:http://theforeman.org/projects/foreman/wiki/Puppet_Facts.
Like Puppet Dashboard, Foreman is a Rails application and can run using a variety of servers, including the in-built Webrick server and an external server such as Apache running Passenger.
To run Foreman with Webrick, change into the root of the Foreman application, usually/usr/share/foreman, and run:
$ sudo ./script/server -e production
Or, you can run the supplied init script to achieve the same result:
$ sudo service foreman start
This will start Foreman on the local host running on port 3000. You can then place Apache or another proxy in front of it if required.
Running Foreman using Apache and Passenger is a more performant and scalable solution. Levy has included some examples of how to configure Foreman for use with Apache and Passenger, including making the Puppet module we discussed earlier capable of automatically configuring Foreman and Passenger (https://github.com/ohadlevy/puppet-foreman).
Once Foreman is running, you should see the home page displayed in
Figure 7-8
.
Figure 7-8.
The Foreman
Foreman has a lot of features that you can use to manage your environment, including recently-added capabilities to manage DNS and DHCP for provisioned hosts. We're going to cover the highlights of its functionality, focusing on its integration with Puppet, including:
- Using Foreman as an External Node Classifier
- Displaying reports in Foreman
- Displaying nodes in Foreman
- Using Foreman to trigger Puppet runs
You can read more about the overall functionality athttp://theforeman.org/projects/foreman/wiki/Features.
Like Puppet Dashboard, Foreman can be used as an ENC. To do that, click on the Hosts tab to display the list of hosts currently in Foreman, as shown in
Figure 7-9
.
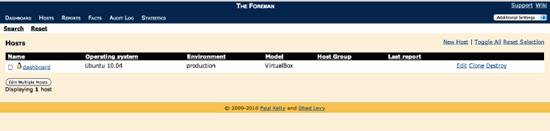
Figure 7-9.
Foreman's Hosts display
You can add hosts to Foreman by clicking the New Host link, shown in
Figure 7-10
.
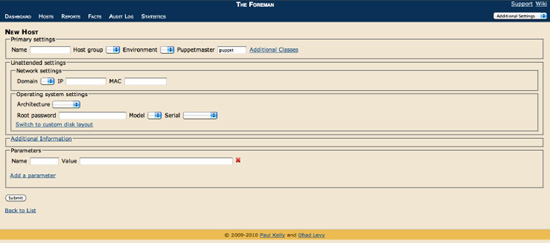
Figure 7-10.
Adding a new host to Foreman
Populate the environment, the required classes and any proposed parameters, and click Submit to add the new host. You can also define global and per domain parameters in the Settings tab. If you define more than one parameter with the same name, Foreman has a hierarchical override structure with parameters processed in order of global, domain, and host, with the last one processed setting the value.
In addition to this manual configuration, Foreman can also import some information from your existing Puppet information so you can pre-seed your external node classifier. To import all the classes contained in your Puppet modules, run the following Rake task:
$ sudo RAILS_ENV=production rake puppet:import:puppet_classes
This task will include all classes in modules specified in yourmodulepath.
Once you have defined your hosts, you need to specify Foreman as the ENC for your Puppet instance. To do this, update thepuppet.confconfiguration file on the Puppet master:
[master]
node_terminus = exec
external_nodes = /usr/share/theforeman/extras/puppet/foreman/files/external_node.rb
 Note
Note
On Puppet 0.25.x and earlier the section is called[puppetmasterd].
Theexternal_node.rbscript is an ENC that is provided with Foreman. It assumes your Foreman instance is running on a host namedforemanon port 3000. Adjust this line to point it at your actual Foreman instance: