Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis (1043 page)
Authors: Mary A. Williamson Mt(ascp) Phd,L. Michael Snyder Md

BOOK: Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis
4.16Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
TABLE 16–52. Percent Activity Distribution of LD Isoenzymes in Tissue
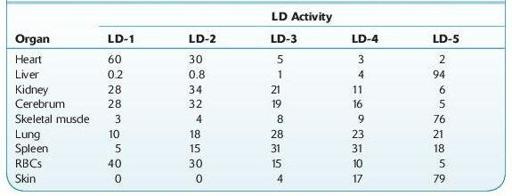
Use
LD is useful in the investigation of a variety of diseases involving the heart, liver, muscle, kidney, lung, and blood; and differentiating heart-synthesized LD from liver and other sources of LD.
Isoenzymes are used by many clinicians in the diagnosis of MI in combination with total CK and CK-MB.
Investigating unexplained causes of LD elevations.
Detection of macro-LD.
Interpretation
See Table 16.53.
Macroenzymes, high molecular weight complexes, occur with LD as well as with CK and other enzymes. LD isoenzymes may complex to IgA or IgG. Such LD macroenzymes are characterized by abnormal position of isoenzyme bands, broadening or abnormal motility of a band, and otherwise unexplained increase of total serum LD. Some of these patients have abnormal ANA results and IgG complexes. Some have abnormalities of light chains but not in amounts that are useful for diagnosis. Treatment with streptokinase was found to produce an LD-streptokinase complex, which was seen as a band at the origin in electrophoresis.
Increased total LD with normal distribution of isoenzymes may be seen in myocardial infarction, arteriosclerotic heart disease with chronic heart failure, and various combinations of acute and chronic diseases (this may represent a general stress reaction).
About 50% of patients with malignant tumors have altered LD patterns. This change often is nonspecific and of no diagnostic value. Solid tumors, especially those of germ cell origin, may increase LD-1.
In megaloblastic anemia, hemolysis, renal cortical infarction, and some patients with cancer, the isoenzyme pattern may mimic that of MI, but the time to peak value and the increase help to differentiate these conditions.
An isoenzyme band cathodal to LD-5 has been called LD-6. It is not an immunoglobulin complex. It has occurred in subjects with liver disease and is said to indicate a grave prognosis.
TABLE 16–53. LD Isoenzyme Patterns in Various Disease Conditions
Other books
The Eunuch's Ward (The String Quartet) by Smyth, Silver
Bones of the Earth by Michael Swanwick
None Left Behind by Charles W. Sasser
Creatures of Snow by Dr. Doctor Doctur
Unleashed by Sara Humphreys
The Gates by Rachael Wade
Pets by Bragi Ólafsson
Post-Human Series Books 1-4 by David Simpson
Can't Hurry Love by Christie Ridgway
Shields of Pride by Elizabeth Chadwick