Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis (1162 page)
Authors: Mary A. Williamson Mt(ascp) Phd,L. Michael Snyder Md

BOOK: Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis
7.17Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
Natural steroid hormone that induces secretory changes in endometrium, promotes mammary gland development, relaxes uterine smooth muscles, blocks follicular maturation, and maintains pregnancy. Hormone synthesized by the ovary; low in follicular phase but increases to 10–40 mg/day during luteal phase and ≤300 mg/day if pregnancy occurs.

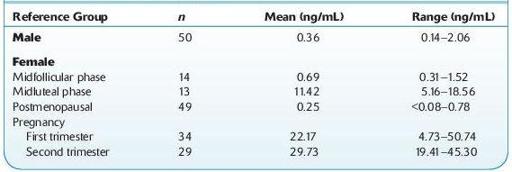
Normal range:
see Table 16.68.
TABLE 16–68. Normal Ranges of Progesterone
Use
Detection of ovulation in the evaluation of the function of the corpus luteum
Monitoring patients having ovulation during induction with hCG, human menopausal gonadotropin, FSH/LH-releasing hormone, or clomiphene
To evaluate patients at risk for early abortion
Interpretation
Increased In
Luteal phase of menstrual cycle
Luteal cysts of the ovary; ovarian tumors (e.g., arrhenoblastoma)
Adrenal tumors
CAH caused by 21-hydroxylase, 17-hydroxylase, and 11-beta hydroxylase
Molar pregnancy
Other books
Chosen by P.C. Cast and Kristin Cast, Kristin Cast
Wanting by Sarah Masters
Adders on the Heath by Gladys Mitchell
Dead Hunger III: The Chatsworth Chronicles by Eric A. Shelman
Interzone Science Fiction and Fantasy Magazine #226 by TTA Press Authors
The Truth About Ever After by Rachel Schurig
To Catch a Highlander by Karen Hawkins
ControlledBurn by Em Petrova
The Numbered Account by Ann Bridge
Amber (Jewel Trilogy, Book 3) by Royal, Lauren