Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis (1233 page)
Authors: Mary A. Williamson Mt(ascp) Phd,L. Michael Snyder Md

BOOK: Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis
12.17Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
Its usefulness has been demonstrated since it reduces the number of red cell or platelet transfused during open heart surgery or shortly after its termination.
THYROGLOBULIN (Tg)
Definition
Heterogeneous iodoglycoprotein secreted only by thyroid follicular cells that is involved in iodination and synthesis of thyroid hormones. It is proportional to thyroid mass.

Normal value:
<55 ng/mL.
Use
To assess the presence and possibly the extent of residual or recurrent or metastatic follicular or papillary thyroid carcinoma after therapy. In patients with these carcinomas treated with total thyroidectomy or radioiodine and taking thyroid hormone therapy, Tg is undetectable if functional tumor is absent but is detected by sensitive immunoassay if functional tumor is present. Tg correlates with tumor mass with highest values in patients with metastases to bones and lungs.
To diagnose factitious hyperthyroidism: Tg is very low or not detectable in factitious hyperthyroidism and is high in all other types of hyperthyroidism (e.g., thyroiditis, Graves disease).
To predict outcome of therapy for hyperthyroidism; higher remission rates in patients with lower Tg values. Failure to become normal after drug-induced remission suggests relapse after drugs are discontinued.
To diagnose thyroid agenesis in newborn.
Interpretation
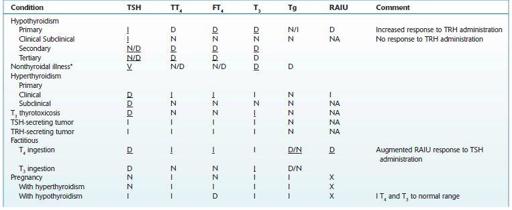
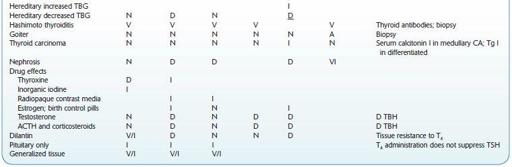
See Table 16.76.
TABLE 16–76. Thyroid Function Tests in Various Conditions
Other books
Breaking the Chain by C D Ledbetter
Heavy Artillery Husband by Debra Webb
Give the Devil His Due (The Sanheim Chronicles, Book Three) by Blackwell, Rob
Wicked Ties (Steele Security Series) by Justice, A.D.
Lethal by Sandra Brown
Magick (The Unwanted Series Book 1) by Mira Monroe
Trouble In Spades by Heather Webber
Rowena (Regency Belles Series Book 1) by Caroline Ashton
Death from a Top Hat by Clayton Rawson