Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis (733 page)
Authors: Mary A. Williamson Mt(ascp) Phd,L. Michael Snyder Md

BOOK: Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis
9.81Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
BENZODIAZEPINES
*
Definition
A class of drugs with a three-ringed chemical structure consisting of a benzene ring, a seven-member diazepine ring, and a phenyl ring attached to the 5-position of the diazepine ring. The CNS depressant activity of these drugs is mediated through the neurotransmitter, GABA.
Specific agents: alprazolam (Xanax), chlordiazepoxide (Librium), diazepam (Valium), temazepam (Restoril), oxazepam (Serax), flunitrazepam (Rohypnol), lorazepam (Ativan), midazolam (Versed), clonazepam (Klonopin), and triazolam (Halcion).

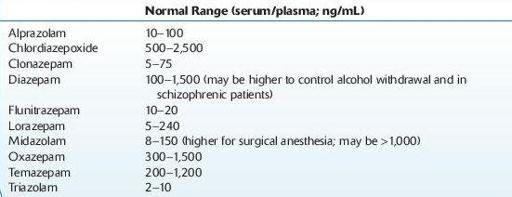
Normal range:
see Table 16.11.
TABLE 16–11. Reference Ranges of Benzodiazepines
Use
Assistance in the treatment of panic attacks, panic disorders, and agoraphobia (alprazolam, clonazepam)
Treatment of anxiety (diazepam, lorazepam)
Treatment of seizures (diazepam, clonazepam)
Treatment of insomnia (temazepam, triazolam)
Preoperative sedation and to assist in induction of surgical anesthesia (midazolam, diazepam, lorazepam)
Muscle relaxant (diazepam)
Treatment of alcohol dependence (chlordiazepoxide, diazepam)
Other books
Other Paths to Glory by Anthony Price
Another Piece of My Heart by Jane Green
Mrs. Poe by Lynn Cullen
An Eye for Danger by Christine M. Fairchild
Jake Walker's Wife by Lough, Loree
The War Planners by Andrew Watts
Johnson Family 1: Unforgettable by Delaney Diamond
New and Selected Poems by Charles Simic
Danger at Dahlkari by Jennifer Wilde
Amadís de Gaula by Garci Rodríguez de Montalvo