Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis (933 page)
Authors: Mary A. Williamson Mt(ascp) Phd,L. Michael Snyder Md

BOOK: Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis
3.5Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
Commonly Used Cluster of Differentiation (CD) Antigens
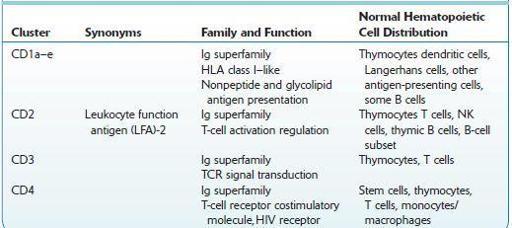
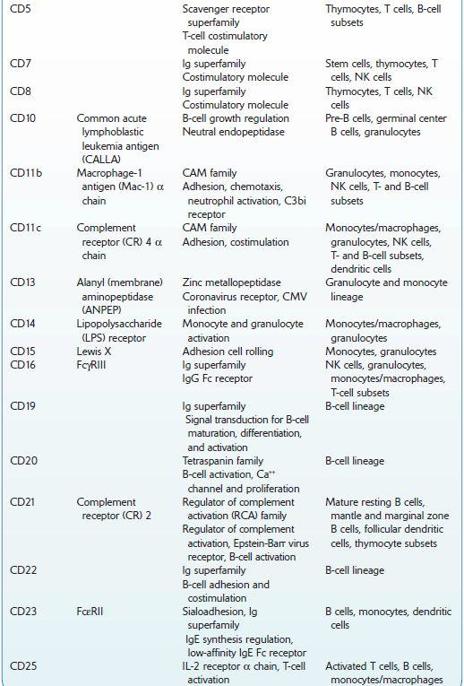
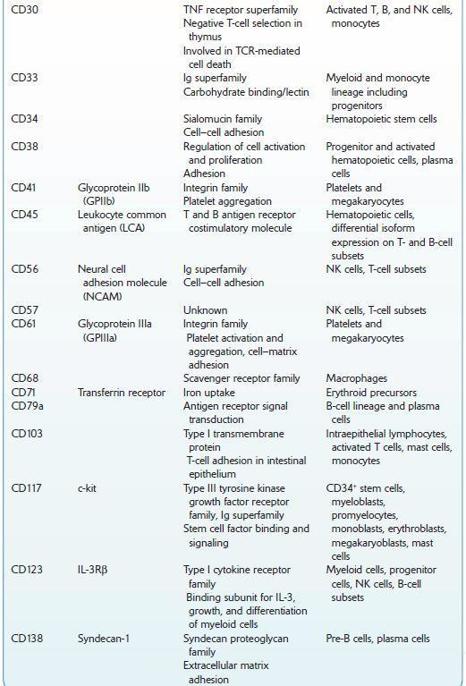
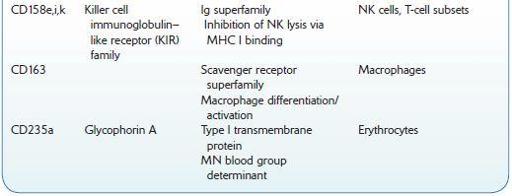
FOLATE, SERUM AND ERYTHROCYTES (RBCs)
Definition
Folate refers to all derivatives of folic acid. Folate is an essential vitamin present in a wide variety of foods such as dark leafy vegetables, citrus fruits, yeast, beans, eggs, and milk. Folate is vital to normal cell growth and DNA synthesis. A folate deficiency can lead to megaloblastic anemia and ultimately to severe neurologic problems. Folate levels in both serum and RBCs are used to assess folate status. The serum folate level is an indicator of recent folate intake. RBC folate is the best indicator of long-term folate stores. A low RBC folate value may indicate a prolonged folate deficiency. Other names: vitamin B
9
.

Normal range:
Serum folate: >6.5 ng/mL
RBC folate: 280–903 ng/mL
Use
Evaluation of folate deficiency
Interpretation
Increased In
Blind loop syndrome
Other books
Martyr by A. R. Kahler
Miss Impractical Pants by Katie Thayne
The Rebel of Rhada by Robert Cham Gilman
When We Were Real (Author's Preferred Edition) by William Barton
Hammer Down: Children of the Undying: Book 2 by Moira Rogers
Shadowborn by Sinclair, Alison
Unforgiven (The Forbidden Bond 2) by Cat Miller
Highlander Most Wanted by Maya Banks
Protecting His Witness (Red Stone Security Series) by Reus, Katie
The Firm: The Troubled Life of the House of Windsor by Penny Junor