Breast Imaging: A Core Review (11 page)
Read Breast Imaging: A Core Review Online
Authors: Biren A. Shah,Sabala Mandava
Tags: #Medical, #Radiology; Radiotherapy & Nuclear Medicine, #Radiology & Nuclear Medicine

A. If fat necrosis is to occur mammographically, it typically occurs within the 1st year.
B. Nipple elevation occurs because there is more skin inferior to the nipple than superior.
C. Architectural distortion commonly presents as a swirled fibroglandular pattern in the inferior and lateral breast.
D. There is parenchymal redistribution of the fibroglandular tissue, as the residual breast tissue is shifted from the upper outer breast to the upper inner breast.
6
A 30-year-old female has a family history of breast cancer in her mother at age 45 and her sister at age 42. She undergoes genetic testing and discovers she is a carrier of the BRCA2 mutation. At what age should she begin screening mammography?
A. 30
B. 32
C. 35
D. 40
7
Breast MRI has proven to be a powerful adjunct to screening mammography in women considered to be at increased risk for breast cancer. Current guidelines recommend screening breast MRI to begin at the age of 30 for which of the following groups?
A. Proven carriers of the BRCA mutation
B. Women with >10% lifetime risk for breast cancer on the basis of family history
C. Women with history of chest irradiation
D. Women with a personal history of biopsy proven atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH)
8
Which of the following is correct regarding performing periodic mammographic surveillance of a BI-RADS 3 (probably benign) lesion versus performing tissue biopsy?
A. Decreased call-back rates
B. Increased costs
C. Increased false positives
D. Increased morbidity
E. Increased positive predictive value
9
Which one of the following breast lesions can be appropriately categorized as a BI-RADS 3 (probably benign) lesion?
A. A nonpalpable, circumscribed mass on a baseline mammogram
B. A nonpalpable, circumscribed mass, new since the last mammogram
C. A nonpalpable, circumscribed mass, unchanged for 2 years
D. A nonpalpable, noncircumscribed mass on a baseline mammogram
E. A palpable, noncircumscribed mass, new since last mammogram
10
Which statement is correct regarding computer-aided detection (CAD) in mammography?
A. CAD sensitivity is greater for masses than calcifications.
B. Breast cancer detection rate increases with CAD.
C. Use of CAD decreases the recall rate.
D. CAD can be used as a primary tool in reading mammograms.
E. CAD makes no false-positive or false-mark findings.
11
Which statement is correct regarding male breast cancer?
A. Gynecomastia is a known risk factor.
B. Male breast cancer is about 10% of all male cancers in the United States.
C. Female relatives of men with breast cancer have no increased risk of breast cancer.
D. It has no associations with BRCA2 gene mutation.
E. Testicular diseases such as undescended testes and testicular injury are considered risk factors for male breast cancer.
12
Which is the most common cancer found in men?
A. Invasive ductal carcinoma
B. Invasive lobular carcinoma
C. Paget disease of the nipple
D. Atypical ductal hyperplasia
13
Which BI-RADS assessment category is inappropriate to assign to a screening mammogram?
A. 0
B. 1
C. 3
D. 5
14
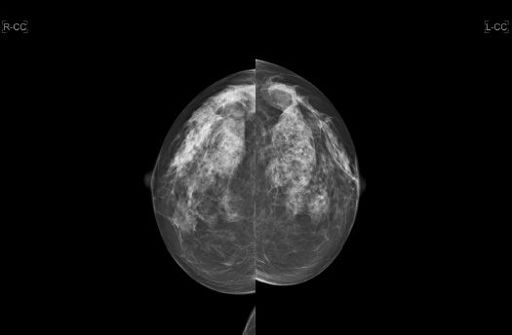
A 43-year-old female presents for a screening mammogram. No prior studies are available. Based on these images, what would be a possible associated finding in this patient?
A. Bilateral acoustic neuromas
B. Increased risk for meningiomas
C. Ependymomas
D. Lisch nodules
15
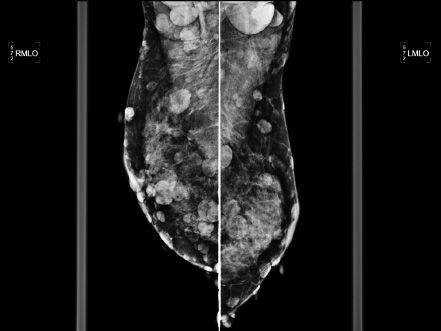
A 46-year-old Asian female presents for a screening mammogram. Patient recently moved to the United States and prior imaging studies were not available for comparison. Ultrasound demonstrates diffuse shadowing. Which of the following is correct?
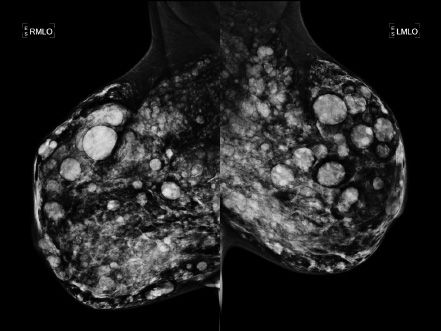
A. Patient has cafe au lait spots and similar mammographic imaging findings in family members.
B. Patient experiences cyclic breast pain predominantly during her premenstrual phase.
C. Patient has a history of prior malignant skin lesion on the sole of her foot.
D. Patient has a history of prior breast procedure.
E. Patient has a history of renal transplant with cyclosporin A therapy.
16a
A 42-year-old female requests contrast-enhanced MRI of the breasts. The patient’s medical history includes a history of fibromyalgia, which makes mammograms very uncomfortable. The patient has a family history of breast cancer affecting her maternal aunt and cousin. The patient’s last screening mammogram demonstrated heterogeneously dense breasts. She has a history of non-Hodgkin lymphoma as a teenager, in complete remission since. Surgical history includes bilateral silicone breast implant placement at 27 years of age. Which of the following is correct?
A. The test is not indicated, and advise the patient to consult with her primary care physician for follow-up, including a clinical breast exam.
B. The test is not indicated, and recommend routine annual screening mammogram.
C. The test is indicated, and advise the patient to schedule her MRI during days 4 to 11 of her menstrual cycle.
D. The test is indicated, and advise the patient to schedule her MRI during days 21 to 28 of her menstrual cycle.
16b
Which of the following is an indication for contrast-enhanced screening MRI in this patient?
A. Her family history of breast cancer
B. Heterogenously dense breasts
C. History of fibromyalgia, making mammograms very uncomfortable
D. History of non-Hodgkin lymphoma
E. Bilateral silicone breast implants
17
An 82-year-old female asks her internist if she needs to have a yearly screening mammogram done. What are the ACS guidelines?
A. No need to have a screening mammogram done after age 75.
B. She should have a screening mammogram done, but once every 2 years.
C. Continue having yearly screening mammograms until age 90, then stop.
D. Continue having yearly screening mammograms done as long as she is in otherwise good health.
18
A 45-year-old female presents for a screening mammogram. A mass is noted and after further imaging and biopsy proves to represent an invasive ductal carcinoma. Which of the following statements is correct regarding the location of this mass?
Other books
The Fugitive Heiress by Amanda Scott
The Ice Museum by Joanna Kavenna
Inferno by Stormy Glenn
Family Blessings by LaVyrle Spencer
Monday the Rabbi Took Off by Harry Kemelman
River City by John Farrow
Embracing Eternity by Linger, Voirey
All Around Atlantis by Deborah Eisenberg
El nazi perfecto by Martin Davidson
The Merchant of Menace by Jill Churchill