Build Your Own ASP.NET 3.5 Website Using C# & VB (45 page)
Read Build Your Own ASP.NET 3.5 Website Using C# & VB Online
Authors: Cristian Darie,Zak Ruvalcaba,Wyatt Barnett
Tags: #C♯ (Computer program language), #Active server pages, #Programming Languages, #C#, #Web Page Design, #Computers, #Web site development, #internet programming, #General, #C? (Computer program language), #Internet, #Visual BASIC, #Microsoft Visual BASIC, #Application Development, #Microsoft .NET Framework

Note that the Type property of the RangeValidator control specifies the data type
that’s expected in the control with which it’s associated; if some other data type is
entered into this field, it fails validation. As such, we’ve removed the
CompareValidator we added for this purpose.
ValidationSummary
Imagine we have a form that contains many form fields. If that page contains errors,
it could be difficult for users to figure out which control caused a given error, because
the page is so big. The ValidationSummary control can alleviate this problem by
presenting the user with a list of error messages in one place on the page. Let’s see
the ValidationSummary control in use. Add it to the end of your
Login.aspx
file, like
so:
LearningASP\VB\Login_11.aspx
(excerpt)
Licensed to [email protected]
Using the Validation Controls
245
When the user clicks the
Submit
button, the ValidationSummary is populated
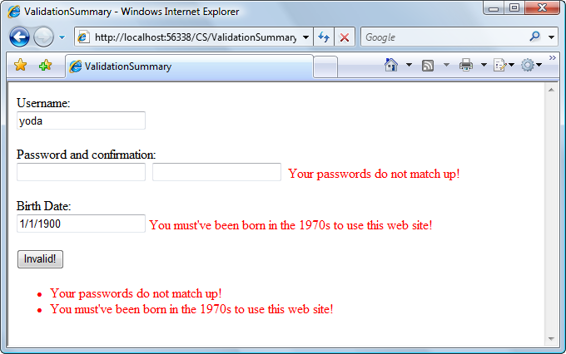
automatically with a list of all the errors on the page, as we can see in Figure 6.7
. Figure 6.7. Using the ValidationSummary control
This control isn’t particularly good looking, but you can see its potential. If you set
the Display properties of all the other validation controls on the page to None, you
could use a ValidationSummary to show all the errors in one place.
If you set the ShowMessageBox property of the ValidationSummary control to True,
the list of errors will be shown in a JavaScript alert
box similar to Figure 6.8
. The server-side list will still be shown to users who don’t have JavaScript-enabled
browsers.
Licensed to [email protected]

246
Build Your Own ASP.NET 3.5 Web Site Using C# & VB
Figure 6.8. Showing validation errors in a dialog
RegularExpressionValidator
The RegularExpressionValidator lets you specify a regular expression that describes all the allowable values for a field. Regular expressions are powerful tools for manipulating strings, and are supported by many programming languages.
They’re commonly used to check for patterns inside strings. Consider, for instance,
the following regular expression:
^\S+@\S+\.\S+$
In plain English, this expression will match any string that begins with one or more
non-whitespace characters followed by the @ character, then one or more nonwhitespace characters, then a dot (.), then one or more non-whitespace characters, followed by the end of the string.
This regular expression describes any one of these email addresses:
However, the regular expression would fail if the user typed in one of these entries:
■ books@sitepoint
■ joe [email protected]
Although regular expressions cannot check to see if the email address itself is valid,
they can, at the very least, provide a means for us to determine whether or not the
user has entered a string of characters that has all the key components of a valid
email address.
Licensed to [email protected]

Using the Validation Controls
247
Let’s change the username field in our login form to an email address field, and
validate it using the RegularExpressionValidator control.
LearningASP\VB\Login_12.aspx
(excerpt)
Email address:
ControlToValidate="emailTextBox"
ErrorMessage="Email address is required!"
SetFocusOnError="True" Display="Dynamic" />
runat="server" ControlToValidate="emailTextBox"
ValidationExpression="^\S+@\S+\.\S+$"
ErrorMessage="You must enter a valid email address!" />
The important property within this control is ValidationExpression, to which we
assign the regular expression that’s appropriate for handling our custom validation
functionality
. Figure 6.9
shows the error message that appears when a user enters an incorrect email address.
Figure 6.9. Using the RegularExpressionValidator control
Licensed to [email protected]
248
Build Your Own ASP.NET 3.5 Web Site Using C# & VB
Some Useful Regular Expressions
Writing regular expressions can be tricky, and a comprehensive discussion of the
topic is outside the scope of this book. Many of the regular expressions presented
here are nowhere near as rigorous as they could be, but they’re still quite useful.
The book
Mastering Regular Expressions
, by Jeffrey E. F. Friedl, contains a single
expression for checking email addresses that tops 6,000 characters!1
Table 6.1
outlines the usage of some simple regular expressions.
Table 6.1. Some simple regular expressions
Description
Regular Expression
email address
^\S+@\S+\.\S+$
web URL
^https?://\S+\.\S+$
US phone numbers ((
555
)
555
-
5555
or
^\(?\d{3}\)?(\s|-)\d{3}-\d{4}$
555
-
555
-
5555
)
international phone numbers (begins with a digit,
^\d(\d|-){7,20}$
followed by between seven and 20 digits and/or
dashes)
five-digit ZIP code
^\d{5}$
nine-digit ZIP code
^\d{5}-\d{4}$
either five-digit or nine-digit ZIP code
^(\d{5})|(\d{5}\-\d{4})$
US social security number
^\d{3}-\d{2}-\d{4}$
Take a close look at the components of the regular expressions in
Table 6.2, and
you should begin to see how they work. If you’d like more information on regular
expressions, try the following resources:
a searchable library of regular expressions
Using Regular Expressions in PHP
3
a great article on the use of regular expressions and PHP
1 Jeffrey E. F. Friedl,
Mastering Regular Expressions
, Third Edition (Sebastopol: O’Reilly Media), 2006. 2 http://www.regexlib.com/
3 http://www.sitepoint.com/article/regular-expressions-php
Licensed to [email protected]
Using the Validation Controls
249
Regular Expressions in JavaScript
4
another great article, this time on the use of regular expressions with JavaScript
Table 6.2. Common regular expression components and their descriptions
Special Character
Description
.
any character
^
beginning of string
$
end of string
\d
numeric digit
\s
whitespace character
\S
non-whitespace character
(abc)
the string abc as a group of characters
?
preceding character or group is optional
+
one or more of the preceding character or group
*
zero or more of the preceding character or group
{
n
}
exactly
n
of the preceding character or group
{
n
,
m
}
n
to
m
of the preceding character or group
(
a
|
b
)
either
a
or
b
\$
a dollar sign (as opposed to the end of a string). We can
escape
any of the
special characters listed above by preceding it with a backslash. For example,
\. matches a period character, \? matches a question mark, and so on.
You’ll find a complete guide and reference to regular expressions and their components in the .NET Framework SDK Documentation.
CustomValidator
The validation controls included with ASP.NET allow you to handle many kinds
of validation, yet certain types of validation cannot be performed with these builtin controls. For instance, imagine that you needed to ensure that a new user’s login details were unique by checking them against a list of existing usernames on the
server. The CustomValidator control can be helpful in this situation, and others
like it. Let’s see how:
4 http://www.sitepoint.com/article/expressions-javascript
Licensed to [email protected]
250
Build Your Own ASP.NET 3.5 Web Site Using C# & VB
Visual Basic
LearningASP\VB\CustomValidator.aspx
(excerpt)
<%@ Page Language="VB" %>
"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
C#
LearningASP\CS\CustomValidator.aspx
(excerpt)