Fundamentals of Midwifery: A Textbook for Students (69 page)
Read Fundamentals of Midwifery: A Textbook for Students Online
Authors: Louise Lewis

BOOK: Fundamentals of Midwifery: A Textbook for Students
2.28Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
Watch, listen and feel the progress of a woman’s labour, and your craftsmanship as a midwife
will develop rapidly.
Conclusion
Caring for a birthing woman brings many midwives immense pleasure in their professional role.
It is an emotive time, laced with hard work, assessing risks and monitoring signs of wellbeing. Within the parameters of normality a midwife has a great opportunity to minimise unnecessary interventions and protect the birthing environment. Observing birthing behaviour through its phases as well as the bio-physical observations ensures that compassionate, woman-centred

159
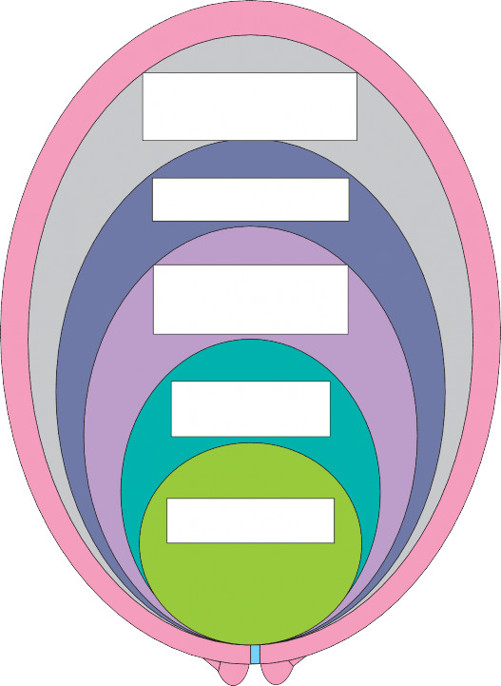
Formulate rationale

160
Evidence based practice/Experiential knowledge of woman and Midwife/Women’s intuitive view/Midwives (professionals) Impression/Benefits, Risks and Alternatives - Collective understanding
Evidence based practice/Experiential knowledge of woman and Midwife/Women’s intuitive view/Midwives (professionals) Impression/Benefits, Risks and Alternatives - Collective understanding
Psychological
Perception, fear, beliefs, emotions, expectations, coping strategies, relationships and interpersonal dynamics
Perception, fear, beliefs, emotions, expectations, coping strategies, relationships and interpersonal dynamics
Physiological
Breathing and relaxation, one to one support, nourishment and fluids, position and movement, massage, birthing ball, Pharmacological/Non-pharmacological pain management
Breathing and relaxation, one to one support, nourishment and fluids, position and movement, massage, birthing ball, Pharmacological/Non-pharmacological pain management
Environment
Un-stimulating, dim lights, use of complementary therapies, quiet, music, feeling safe, nesting Endorphins/Oxytocin/Adrenaline
Un-stimulating, dim lights, use of complementary therapies, quiet, music, feeling safe, nesting Endorphins/Oxytocin/Adrenaline
Behaviour
Talkative, Descriptive, Dependant, Tearful, Excited, Tired, Movement, Unsure, Happy
Talkative, Descriptive, Dependant, Tearful, Excited, Tired, Movement, Unsure, Happy
Figure 7.9
Concept map guideline for decision-making in normal labour.
care is provided, leading to a better potential for women to feel they have had some control. A midwife, therefore, can help the woman to achieve an optimal hormonal balance, even when medical intervention is needed to assist the birthing process, ensuring the best outcomes for mother and baby and satisfaction with the experience.
End of chapter activities
Crossword

161
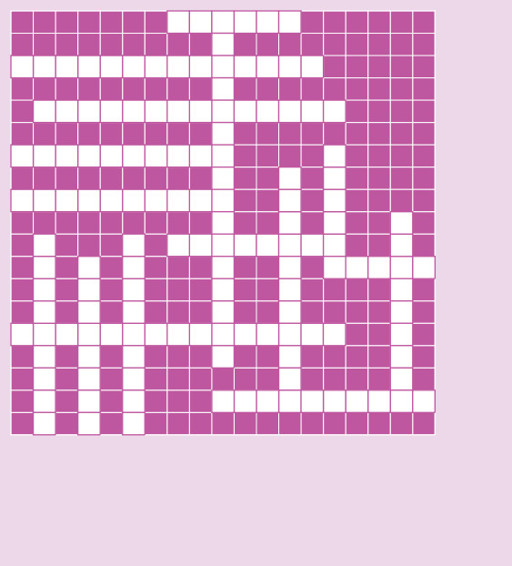
1 2
3
4
5 6
7
8
9
10 11 12
13 14
15
16
Across
1.
Stage of labour when the cervix is fully dilated until the birth of the baby
Biofeedback mechanism
Chemicals which have roles in the central nervous system and sympathetic nervous system
Hormone which stimulates the sympa- thetic nervous system
8.
Describing the phases between the stages of labour
Person in control during labour and birth162
Stage of labour involving delivery of theplacenta and membranes
Electronic monitoring of the fetal heart
Down
2.
Surgical operation where the baby is deliv- ered via an incision in the abdomen
Down
2.
Surgical operation where the baby is deliv- ered via an incision in the abdomen
The phase when the cervix is effacing in the presence of the hormone prostaglandin
The arrest of bleeding involving blood coagulation and contraction of blood vessels

 16.
16.
Surgical incision to widen the vaginalorifice

 16.
16.Surgical incision to widen the vaginalorifice
Includes a graphical record of progress oflabour
What midwives should be facilitating and maintaining
Artificial rupture of the amniotic sac
13.
A regional anaesthetic
Find out more
Below is a list of things you can find out about to enhance your knowledge of the issues and topics covered in this chapter. Make notes using the chapter content, the references and further reading identified, local policies and guidelines and discussions with colleagues.
1.
Read the Hospital Trust guideline/policy for midwifery-led care in labour.
2.
Read the Royal College of Midwives (2012) Evidence-based guidelines for midwifery-led care in labour.
3.
Find out what resources are available to facilitate an active birth in the area you are working.
4.
Find out about the local provision for birth preparation for pregnant women and birth partners.
 Glossary of terms
Glossary of terms

 Acupuncture
Acupuncture
Acupuncture is a form of ancient Chinese medicine in which fine needles are inserted into the skin at certain points on the body. It is a complementary therapy.


 Adrenaline
Adrenaline
Hormone secreted by adrenal gland, which stimulates the sympathetic nervous system.

 Amniotomy
Amniotomy
Artificial rupture of the amniotic sac.
Caesarean section
Surgical operation where the baby is delivered via an incision in the abdomen.
Cardiotocograph
Electronic monitoring of the fetal heart.


 Catecholamines
Catecholamines
Chemicals which have roles in the central nervous system and sympathetic nervous system.
 Craftmanship
Craftmanship
A person who is skilled.

13.
A regional anaesthetic
Find out more
Below is a list of things you can find out about to enhance your knowledge of the issues and topics covered in this chapter. Make notes using the chapter content, the references and further reading identified, local policies and guidelines and discussions with colleagues.
1.
Read the Hospital Trust guideline/policy for midwifery-led care in labour.
2.
Read the Royal College of Midwives (2012) Evidence-based guidelines for midwifery-led care in labour.
3.
Find out what resources are available to facilitate an active birth in the area you are working.
4.
Find out about the local provision for birth preparation for pregnant women and birth partners.
 Glossary of terms
Glossary of terms
 Acupuncture
AcupunctureAcupuncture is a form of ancient Chinese medicine in which fine needles are inserted into the skin at certain points on the body. It is a complementary therapy.


 Adrenaline
AdrenalineHormone secreted by adrenal gland, which stimulates the sympathetic nervous system.

 Amniotomy
AmniotomyArtificial rupture of the amniotic sac.
Caesarean section
Surgical operation where the baby is delivered via an incision in the abdomen.
Cardiotocograph
Electronic monitoring of the fetal heart.


 Catecholamines
CatecholaminesChemicals which have roles in the central nervous system and sympathetic nervous system.
 Craftmanship
CraftmanshipA person who is skilled.

Other books
Las aventuras de Tom Bombadil y algunos poemas del Libro Rojo by J.R.R. Tolkien
A Duchess Enraged by Alicia Quigley
Savior by Eli Harlow
Deluge by Anne McCaffrey
Summer of Love by Fforde, Katie
Nobody's Hero by Kallypso Masters
The Hunt by Ellisson, C.J.
Drat! You Copycat! by Nancy Krulik
Love Beyond Loyalty by Rebecca Royce
Tyme's End by B. R. Collins