Modern Mind: An Intellectual History of the 20th Century (44 page)
Read Modern Mind: An Intellectual History of the 20th Century Online
Authors: Peter Watson
Tags: #World History, #20th Century, #Retail, #Intellectual History, #History

In the early days the notion of the BBC as a public service was very uncertain. Ad manner of forces were against it. For a start, the country’s mood was volatile. Britain was still in financial straits, recovering from the war, and 1.5 million were unemployed. Lloyd George’s coalition government was far from popular, and these overall conditions led to the general strike of 1926, which itself imperilled the BBC. A second factor was the press, which viewed
the BBC as a threat, to such an extent that no news bulletins were allowed before 7:00
P.M.
Third, no one had any idea what sort of material should be broadcast – audience research didn’t begin until 1936, and ‘listening in,’ as it was called, was believed by many to be a fad that would soon pass.
50
Then there was the character of the Corporation’s first director, a thirty-three-year-old Scottish engineer named John Reith. Reith, a high-minded Scottish Presbyterian, never doubted for a moment that radio should be far more than entertainment, that it should also educate and inform. As a result, the BBC gave its audience what Reith believed was needed rather than what the people wanted. Despite this high-handed and high-minded approach, the BBC proved popular. From a staff of 4 in the first year, it grew to employ 177 twelve months after that. In fact, the growth of radio actually outstripped that of television a generation or so later, as these figures show:
51
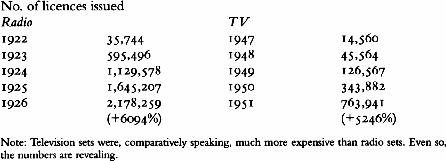
To be set against this crude measure of popularity, there was a crop of worries about the intellectual damage radio might do. ‘Instead of solitary thought,’ said the headmaster of Rugby School, ‘people would listen in to what was said to millions of people, which could not be the best of things.’
52
Another worry was that radio would make people ‘more passive,’ producing ‘all-alike girls.’ Still others feared radio would keep husbands at home, adversely affecting pub attendance. In 1925
Punch
magazine, referring to the new culture established by the BBC, labelled it as ‘middlebrow.’
53
Editorially speaking, the BBC’s first test arrived in 1926 with the onset of the General Strike. Most newspapers were included in the strike, so for a time the BBC was virtually the only source of news. Reith responded by ordering five bulletins a day instead of the usual one. The accepted view now is that Reith complied more or less with what the government asked, in particular putting an optimistic gloss on government policy and actions. In his official history of the BBC, Professor Asa Briggs gives this example of an item broadcast during the strike: ‘Anyone who is suffering from “strike depression” can do no better than to pay a visit to “RSVP” [a show] at the New Vaudeville Theatre.’ Not everyone thought that Reith was a stool pigeon, however. Winston Churchill, then chancellor of the exchequer, actually thought the BBC should be taken over. He saw it as a rival to his own
British Gazette,
edited from his
official address at 11 Downing Street.
54
Churchill failed, but people had seen the danger, and it was partly as a result of this tussle that the ‘C’ in BBC was changed in 1927 from Company to Corporation, protected by royal charter. The General Strike was therefore a watershed for the BBC in the realm of politics. Before the strike, politics (and other ‘controversial’ subjects) were avoided entirely, but the strike changed all that, and in 1929
The Week in Parliament
was launched. Three years later, the corporation began its own news-gathering organisation.
55
The historian J. H. Plumb has said that one of the great unsung achievements of the twentieth century has been the education of vast numbers of people. Government-funded schools and universities led the way here, but the various forms of new media, many of which started in the 1920s, have also played their part. The term
middlebrow
may be intended as an insult by some, but for millions, like the readers of
Time
or those listening in to the BBC, it was more a question of wising up than dumbing down.
*
The history of Harlem was not fully recovered until the 1980s, by such scholars as David Levering Lewis and George Hutchinson. My account is based chiefly on their work.
HEROES’ TWILIGHT
In February 1920 a horror film was released in Berlin that was, in the words of one critic, ‘uncanny, demonic, cruel, “Gothic”,’ a Frankenstein-type story filled with bizarre lighting and dark, distorted sets.
1
Considered by many to be the first ‘art film,’
The Cabinet of Dr Caligari
was a huge success, so popular in Paris that it played in the same theatre every day between 1920 and 1927.
2
But the film was more than a record breaker. As the historian of interwar Germany Peter Gay writes, ‘With its nightmarish plot, its Expressionist sets, its murky atmosphere,
Caligari
continues to embody the Weimar spirit to posterity as palpably as Gropius’s buddings, Kandinsky’s abstractions, Grosz’s cartoons, and Marlene Dietrich’s legs … But
Caligari,
decisive for the history of film, is also instructive for the history of Weimar…. There was more at stake here than a strange script or novelties of lighting.’
3
Following World War I, as we have seen, Germany was turned almost overnight into a republic. Berlin remained the capital but Weimar was chosen as the seat of the assembly after a constitutional conference had been held there to decide the form the new republic would take, because of its immaculate reputation (Goethe, Schiller), and because of worries that the violence in Berlin and Munich would escalate if either of those cities were selected. The Weimar Republic lasted for fourteen years until Hitler came to power in Germany in 1933, a tumultuous interregnum between disasters which astonishingly managed to produce a distinctive culture that was both brilliant and characterised by its own style of thought, the very antithesis of Middletown.
The period can be conveniently divided into three clear phases.
4
From the end of 1918 to 1924, ‘with its revolution, civil war, foreign occupation, and fantastic inflation, [there] was a time of experimentation in the arts; Expressionism dominated politics as much as painting or the stage.’
5
This was followed, from 1924 to 1929, by a period of economic stability, a relief from political violence, and increasing prosperity reflected in the arts by the
Neue Sachlichkeit,
the ‘new objectivity,’ a movement whose aims were matter-of-factness, even sobriety. Finally, the period 1929 to 1933 saw a return to political violence, rising unemployment, and authoritarian government by decree; the arts were cowed into silence, and replaced by propagandistic
Kitsch.
6
*
Caligari
was a collaboration between two men, Hans Janowitz, a Czech, and Carl Meyer, an Austrian, who had met in Berlin in 1919.
7
Their work was not only fiercely antiwar but also explored what expressionism could do in the cinema. The film features the mad Dr Caligari, a fairground vaudeville act who entertains with his somnambulist, Cesare. Outside the fair, however, there is a second string to the story, and it is far darker. Wherever Caligari goes, death is never far behind. Anyone who crosses him ends up dead. The story proper starts after Caligari kills two students – or thinks that he has. In fact, one survives, and it is this survivor, Francis, who begins to investigate. Nosing around, he discovers Cesare asleep in a box. But the killings continue, and when Francis returns to the sleeping Cesare, he realises this time that the ‘person’ motionless in the box is merely a dummy. It dawns on Francis, and the police, whose help he has now enlisted, that the sleepwalking Cesare is unconsciously obeying Caligari’s instructions, killing on his behalf without understanding what he has done. Realising he has been discovered, Caligari flees into an insane asylum. But this is more than it seems, for Francis now finds out that Caligari is also the
director
of the asylum. Shocking as this is, there is no escape for Caligari, and when his double life is exposed, far from being cathartic, he loses all self-control and ends up in a straitjacket.
8
This was the original story of Caligari, but before the film appeared it went through a drastic metamorphosis. Janowitz and Meyer had intended their story to be a powerful polemic against military obedience and assumed that when the script was accepted by Erich Pommer, one of the most successful producers of the day, he would not change it in any way.
9
However, Pommer and the director, Robert Wiene, actually turned the story inside out, rearranging it so that it is Francis and his girlfriend who are mad. The ideas of abduction and murder are now no more than
their
delusions, and the director of the asylum is in reality a benign doctor who cures Francis of his evil thoughts. Janowitz and Meyer were furious. Pommers version of the story was the opposite of theirs. The criticism of blind obedience had disappeared and, even worse, authority was shown as kindly, even safe. It was a travesty.
10
The irony was that Pommer’s version was a great success, commercially and artistically, and film historians have often wondered whether the original version would have done as well. And perhaps there is a fundamental point here. Though the plot was changed, the style of telling the story was not – it was still expressionistic. Expressionism was a force, an impulse to revolution and change. But, like the psychoanalytic theory on which it was based, it was not fully worked out. The expressionist Novembergruppe, founded in December 1918, was a revolutionary alliance of all the artists who wanted to see change – Emil Nolde, Walter Gropius, Bertolt Brecht, Kurt Weill, Alban Berg, and Paul Hindemith. But revolution needed more than an engine; it needed direction. Expressionism never provided that. And perhaps in the end its lack of direction was one of those factors that enabled Adolf Hitler’s rise to power. He hated expressionism as much as he hated anything.
11
But it would be wrong to see Weimar as a temporary way station on the path to Hitler. It certainly did not see itself in that light, and it boasted many
solid achievements. Not the least of these was the establishment of some very prestigious academic institutions, still centres of excellence even today. These included the Psychoanalytic Institute in Berlin – home to Franz Alexander, Karen Horney, Otto Fenichel, Melanie Klein, and Wilhelm Reich – and the Deutsche Hochschule für Politik, which had more than two thousand students by the last year of the republic: the teachers here included Sigmund Neumann, Franz Neumann, and Hajo Holborn. And then there was the Warburg Institute of Art History.
In 1920 the German philosopher Ernst Cassirer paid a visit to the Warburg art historical library in Hamburg. He had just been appointed to the chair in philosophy at the new university in Hamburg and knew that some of the scholars at the library shared his interests. He was shown around by Fritz Saxl, then in charge. The library was the fantastic fruit of a lifetime’s collecting by Aby Warburg, a rich, scholarly, and ‘intermittently psychotic individual’ who, not unlike T. S. Eliot and James Joyce, was obsessed by classical antiquity and the extent to which its ideas and values could be perpetuated in the modern world.
12
The charm and value of the library was not just that Warburg had been able to afford thousands of rare volumes on many recondite topics, but the careful way he had put them together to illuminate one another: thus art, religion, and philosophy were mixed up with history, mathematics, and anthropology. For Warburg, Following James Frazer, philosophy was inseparable from study of the ‘primitive mind.’ The Warburg Institute has been the home of many important art historical studies throughout the century, but it started in Weimar Germany, where among the papers published under its auspices were Erwin Panofsky’s
Idea, Dürers ‘Melancolia 1,’ Hercules am Scheidewege
and Percy Schramm’s
Kaiser, Rom und Renovatio.
Panofsky’s way of reading paintings, his ‘iconological method,’ as it was called, would prove hugely influential after World War II.
13
Europeans had been fascinated by the rise of the skyscraper in America, but it was difficult to adapt on the eastern side of the Atlantic: the old cities of France, Italy, and Germany were all in place, and too beautiful to allow the distortion that very tall buildings threatened.
14
But the new materials of the twentieth century, which helped the birth of the skyscraper, were very seductive and proved popular in Europe, especially steel, reinforced concrete, and sheet glass. The latter in particular transformed the appearance of buddings and the experience of being
inside
a structure. With its different colours, reflectivity, and transparency, glass was a flexible, expressive skin for buildings constructed in steel. In the end, glass and steel had a bigger effect on European architects than concrete did, and especially on three architects who worked together in the studio of the leading industrial designer in Germany, Peter Behrens (1868– 1940). These were Walter Gropius, Ludwig Mies van der Rohe, and Charles-Edouard Jeanneret, better known as Le Corbusier. Each would make his mark, but the first was Gropius. It was Gropius who founded the Bauhaus.
It is not difficult to see why Gropius should have taken the lead. Influenced by Marx and by William Morris, he always believed, contrary to Adolf Loos, that craftsmanship was as important as ‘higher’ art. He had also learned from
Behrens, whose firm was one of the first to develop the modern ‘design package,’ providing AEG with a corporate style that they used for everything, from letterheads and arc lamps to the company’s buildings themselves. Therefore, when the Grand Ducal Academy of Art, which was founded in the mid-eighteenth century, was merged with the Weimar Arts and Crafts School, established in 1902, he was an obvious choice as director. The fused structure was given the name Staatliche Bauhaus, with
Bauhaus —
literally, ‘house for building’ – chosen because it echoed the
Bauhütten,
mediaeval lodges where those constructing the great cathedrals were housed.
15
The early years of the Bauhaus, in Weimar, were troubled. The government of Thuringia, where Weimar was located, was very right-wing, and the school’s collectivist approach, the rebelliousness of its students, and the style of its first head teacher, Johannes Itten, a quarrelsome mystic-religious, proved very unpopular.
16
The school’s budget was cut, forcing its removal to Dessau, which had a more congenial administration.
17
This change in location seems to have brought about a change in Gropius himself. He produced a second manifesto, in which he announced that the school would concern itself with practical questions of the modern world – mass housing, industrial design, typography, and the ‘development of prototypes.’ The obsession with wood was abandoned: Gropius’s design for the school’s new building was entirely of steel, glass, and concrete, to underline the school’s partnership with industry. Inside the place, Gropius vowed, students and staff would explore a ‘positive attitude to the living environment of vehicles and machines … avoiding all romantic embellishment and whimsy.’
18
After a lost war and an enormous rise in inflation, there was no social priority of greater importance in Weimar Germany than mass housing. And so Bauhaus architects were among those who developed what became a familiar form of social housing, the
Siedlung
or ‘settlement.’ This was introduced to the world iein 1927, at the Stuttgart trade fair exhibition. Corbusier, Mies van der Rohe, Gropius, J. P. Oud, and Bruno Taut all designed buildings for the Weissenhof (White House)
Siedlung,
‘and twenty thousand people came every day to marvel at the flat roofs, white walls, strip windows and
pilotis
of what Rohe called “the great struggle for a new way of life.” ‘
19
Although the
Siedlungen
were undoubtedly better than the nineteenth-century slums they were intended to replace, the lasting influence of the Bauhaus has been in the area of applied design.
20
The Bauhaus philosophy, ‘that it is far harder to design a first-rate teapot than paint a second-rate picture,’ has found wide acceptance – folding beds, built-in cupboards, stackable chairs and tables, designed with mass-production processes in mind and with an understanding of the buildings these objects were to be used in.
21
The catastrophe of World War I, followed by the famine, unemployment, and inflation of the postwar years, for many people confirmed Marx’s theory that capitalism would eventually collapse under the weight of its own ‘insoluble contradictions’. However, it soon became clear that it wasn’t communism that was appearing from the rubble, but fascism. Some Marxists were so disillusioned
by this that they abandoned Marxism altogether. Others remained convinced of the theory, despite the evidence. But there was a third group, people in between, who wished to remain Marxists but felt that Marxist theory needed reconstructing if it was to remain credible. This group assembled in Frankfurt in the late 1920s and made a name for itself as the Frankfurt School, with its own institute in the city. Thanks to the Nazis, the institute didn’t stay long, but the name stuck.
22
The three best-known members of the Frankfurt School were Theodor Adorno, a man who ‘seemed equally at home in philosophy, sociology and music,’ Max Horkheimer, a philosopher and sociologist, less innovative than Adorno but perhaps more dependable, and the political theorist Herbert Marcuse, who in time would become the most famous of all. Horkheimer was the director of the institute. In addition to being a philosopher and sociologist, he was also a financial wizard, who brilliantly manipulated the investments of the institute, both in Germany and afterward in the United States. According to Marcuse, nothing that was written by the Frankfurt School was published without previous discussion with him. Adorno was the early star. According to Marcuse, ‘When he talked it could be printed without any changes.’ In addition there was Leo Lowenthal, the literary critic of the school, Franz Neumann, a legal philosopher, and Friedrich Pollock, who was one of those who argued – against Marx and to Lenin’s fury – that there were no compelling internal reasons why capitalism should collapse.
23