Secondary Schizophrenia (71 page)
Read Secondary Schizophrenia Online
Authors: Perminder S. Sachdev

schizophrenia. Neuroreport, 1999.
gene: longitudinal evidence of a
of drug choice. J Nerv Ment Dis,
10
(8):1665–9.
gene X environment interaction.
1987.
175
(11):641–52.
53. Dean B.,
et al.
Studies on
Biol Psychiatry, 2005.
57
(10):
[3H]CP-55940 binding in the
1117–27.
43. Verdoux H.,
et al.
Effects of
human central nervous system:
34. Fergusson D., Horwood J.,
cannabis and psychosis
regional specific changes in
Swain-Campbell N. Cannabis
vulnerability in daily life: an
density of cannabinoid-1
dependence and psychotic
experience sampling test study.
receptors associated with
symptoms in young people.
Psychol Med, 2003.
33
(1):23–32.
schizophrenia and cannabis use.
Psychol Med, 2003.
33
(1):
44. Lehman A. F.,
et al.
Rehabilitation
Neuroscience, 2001.
103
(1):
15–21.
for adults with severe mental
9–15.
35. Fergusson D. M., Horwood L. J.,
illness and substance use
54. D’Souza D. C.,
et al.
The
Ridder E. M. Tests of causal
disorders: a clinical trial. J Nerv
psychotomimetic effects of
linkages between cannabis use
Ment Dis, 1993.
181
(2):86–90.
intravenous delta-9-
and psychotic symptoms.
45. Epstein J. N.,
et al.
The effects
tetrahydrocannabinol in healthy
Addiction, 2005.
100
(3):
of anxiety on continuous
individuals: implications for
354–66.
performance test functioning in
psychosis. Neuropsychopharma-
36. Verdoux H., et al., Cannabis use
an ADHD clinic sample. J Atten
cology, 2004.
29
(8):1558–72.
and the expression of psychosis
Disord, 1997.
2
(1):45–52.
55. Negrete J. C.,
et al.
Cannabis
vulnerability in daily life.
46. Jerrell J. M., Ridgely M. S.
affects the severity of
Eur Psychiatry, 2002.
17
:
Comparative effectiveness of three
schizophrenic symptoms: results
180S–180S.
approaches to serving people
of a clinical survey. Psychol Med,
37. Degenhardt L., Tennant C., and
with severe mental illness and
1986.
16
:515–20.
Gilmour S.,
et al.
The temporal
substance abuse disorders.
56. Cleghorn J. M.,
et al.
Substance
dynamics of relationships
J Nerv Ment Dis, 1995.
183
(9):
abuse and schizophrenia: effect
between cannabis, psychosis and
566–76.
on symptoms but not on
depression among young adults
47. Hall W., Degenhardt L., Lynskey
neurocognitive function. J Clin
with psychotic disorders: Findings
M. (2001). The Health and
Psychiatr, 1991.
52
:26–30.
from a ten-month prospective
Psychological Consequences of
57. Jablensky A., Sartorius N.,
study. Psychol Med, 2007.
Cannabis Use. Canberra:
Ernberg G. Schizophrenia:
37
(7):927–34.
Australian Publishing Service.
manifestations, incidence and
38. Mueser K. T., Bellack A. S.,
48. Julien R. (2001). A Primer of Drug
course in different cultures. A
Blanchard J. J. Comorbidity of
Action. A Concise, Nontechnical
World Health Organization
schizophrenia and substance
Guide to the Actions, Uses, and
Ten-Country Study. Psychol Med,
abuse: implications for treatment.
Side Effects of Psychoactive Drugs.
20
(Suppl), 1991.
J Consult Clin Psychol, 1992.
60
(6):
9th ed. New York: Worth
58. Martinez-Arevalo M. J.,
845–56.
Publishers.
Calcedo-Ordonez A., Varo-Prieto
39. Noordsy D. L.,
et al.
Subjective
49. Fritzsche M. Are cannabinoid
J. R. Cannabis consumption as a
experiences related to alcohol
receptor knockout mice animal
prognostic factor in
use among schizophrenics.
models for schizophrenia?
schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry,
J Nerv Ment Dis, 1991.
179
(7):
Med Hypotheses, 2001.
56
(6):
1994.
164
:679–81.
410–14.
638–43.
59. Linszen, D. H., Dingemans P. M.,
40. Dixon L.,
et al.
Acute effects of
50. Glass M. The role of cannabinoids
Lenior M. E., Cannabis abuse
177
drug abuse in schizophrenic
in neurodegenerative diseases.
and the course of recent-onset
Organic Syndromes of Schizophrenia – Section 3
schizophrenic disorders.
schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry,
62. Mueser K., Bellack A., Blanchard
Arch Gen Psychiatry, 1994.
51
:
1992.
149
:552–3.
J. Comorbidity of schizophrenia
273–9.
61. Kavanagh D. An intervention for
and substance abuse: implications
60. Zisook S.,
et al.
Past substance
substance abuse in schizophrenia.
for treatment. J Consult Clin
abuse clinical course of
Behav Change, 1995.
12
:20–30.
Psychol, 1992.
60
(6):845–56.
178
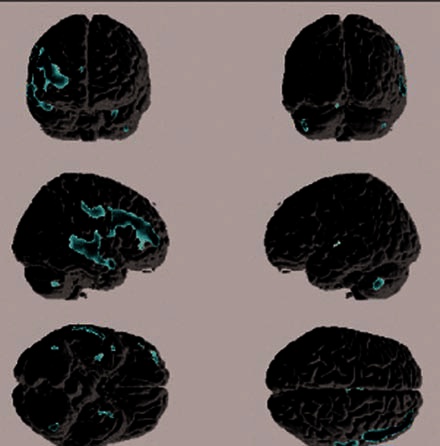
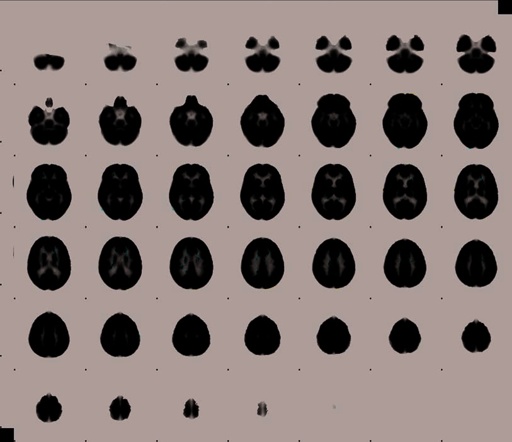
Figure 1.1
Brain MRI images showing grey-matter volume reductions in first-episode schizophrenia subjects compared to healthy controls using Voxel Based Morphometry (VBM). [From the University of
Pittsburgh.]
Figure 5.3
Significance probability mapping [184] test areas of decrease in FDG relative metabolic rate and D2 receptor binding.

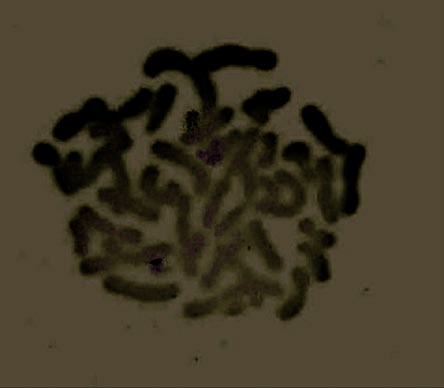
(A)
(B)
Figure 24.3
Fluorescence in-situ hybridization showing the presence of both 22q11.2 regions (a) and the deletion (b) with the
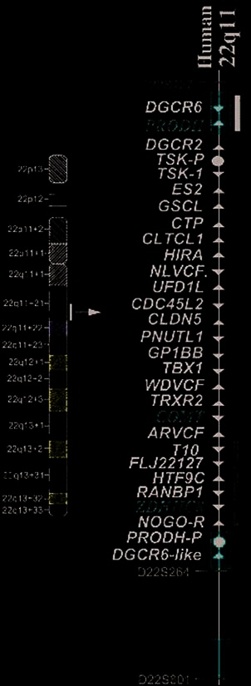
Figure 24.5
Ideogram of Chromosome 22, with a listing of all the commercially available probe (Vysis, Gaithersburg, MD. Courtesy: genes in the 1.5 Mb interval in the q11.2 region, thought to be Mark Pettenati, PhD, Department of Pediatrics, Wake Forest
critical for schizophrenia. The genes denoted in red are thought to University School of Medicine.)
be most likely related to psychosis.
Section 3
Organic syndromes of schizophrenia:
drugs and schizophrenia-like psychosis
12Toxicpsychosis
Rajeev Kumar and Jeffrey C. L. Looi
Facts box
r
Toxic psychosis is characterized by the
A number of terms have been used in literature to
presence of psychotic symptoms usually
describe psychosis associated with acutely impaired
associated with acutely impaired cognitive
cognitive functions
[1].
These include toxic psy-functions.
chosis, acute brain syndrome, acute organic psychosis,
r
acute confusional state, ICU psychosis, metabolic
A number of centrally active prescription
encephalopathy, toxic confusional state, and delirium.
drugs taken in excessive amount can cause
The multiple terms used to denote this state lead
neurotoxicity.
r
to confusion both in clinical and research practice.
Clinical manifestations include delirium with
Therefore, the more recent psychiatric diagnostic and
features of altered consciousness,
classification systems (DSM-IV and ICD-10) opted
impairment of general cognitive functions,
to use the term “delirium.” This chapter reviews the
acute onset, fluctuating course, nocturnal