Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis (1112 page)
Authors: Mary A. Williamson Mt(ascp) Phd,L. Michael Snyder Md

BOOK: Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis
9.12Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
Nonspecific (α-naphthyl butyrate or α-naphthyl acetate) esterase identifies monocytic cells but does not stain granulocytes or eosinophils. These two stains may be used to identify leukemic lineage.
Iron stain (used as Prussian blue reaction). It identifies iron in nucleated red cells (either as siderocytes or as ringed sideroblasts [myelodysplastic syndromes]); it also identifies Pappenheimer bodies in erythrocytes (RBCs, Table 16.73).
Periodic acid–Schiff (PAS): Detects intracellular glycogen and neutral mucosubstances, which are found in most hematopoietic cells. It is helpful in the diagnosis of erythroleukemia because of the intensity of its diffuse staining in primitive erythroid cells.
Limitations
Poorly prepared smears may be difficult to evaluate accurately.
PHOSPHATE, BLOOD
Definition
Phosphate is used in the synthesis of phosphorylated compounds. It accompanies glucose into cells. The total body content in normal adults is approximately 700–800 g. About 80–85% of phosphate is contained in bones; the remaining 15–20% is in ICF in tissue as organic phosphates (phospholipids, nucleic acids, NADP, ATP). Only 0.1% is in the ECF as inorganic phosphate, and only this fraction of phosphorus is measured in routine clinical settings.

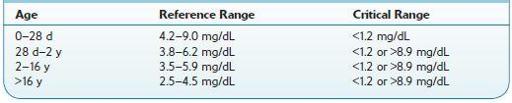
Normal range:
see Table 16.65.
TABLE 16–65. Normal Ranges for Phosphate
Use
Monitoring of blood phosphate level in renal, endocrine, and GI disorders
Interpretation
Increased In
Acute or chronic renal failure (most common cause) with decreased GFR
Other books
Big Girls on Top by Mercy Walker
Great Soul: Mahatma Gandhi and His Struggle With India by Joseph Lelyveld
Your Next-Door Neighbor Is a Dragon by Zack Parsons
In The Wreckage: A Tale of Two Brothers by Simon J. Townley
Overdosed America by John Abramson
Perfect in My Sight by Tanya Anne Crosby
Defying the Odds by Kele Moon
Unwrapped by Evelyn Adams
The Knotty Bride by Julie Sarff
Snowbound Bride-to-Be by Cara Colter