Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis (1218 page)
Authors: Mary A. Williamson Mt(ascp) Phd,L. Michael Snyder Md

BOOK: Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis
4.16Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
SEX HORMONE–BINDING GLOBULIN (SHBG)
Definition
A glycoprotein, synthesized in the liver, which binds testosterone and 5-dihydrotestosterone with high affinity, and estradiol with a somewhat lower affinity. SHBG typically circulates at higher concentrations in women than in men, due to the higher ratio of estrogens to androgens in women. Administration of androgens tends to be associated with decreased SHBG levels. Because variations in the carrier protein levels may affect the concentration of testosterone in circulation, SHBG levels are commonly measured as a supplement to total testosterone determinations. The “free androgen index” (FAI), calculated as the ratio of total testosterone to SHBG, has proved to be a useful indicator of abnormal androgen status in conditions such as hirsutism.

Normal range:
see Table 16.74.
TABLE 16–74. Normal Ranges of Sex Hormone–Binding Globulin
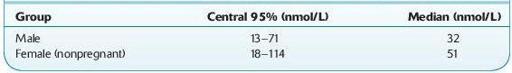
Use
Diagnosis and follow-up of women with symptoms or signs of androgen excess (e.g., polycystic ovarian syndrome and idiopathic hirsutism)
As an adjunct in monitoring sex steroid and antiandrogen therapy
As an adjunct in the diagnosis of disorders of puberty
As an adjunct in the diagnosis and follow-up of anorexia nervosa
Interpretation
Increased In
Hyperthyroidism
Hepatic cirrhosis
Pregnancy
Other books
Sacrifice by Paul Finch
Lovers Premiere (Kimani Romance) by Adrianne Byrd
Tale of the Dead Town by Hideyuki Kikuchi
Gone Cold by Douglas Corleone
Z. Apocalypse by Steve Cole
Almost Persuaded: Miss Mary King by P. O. Dixon
Against the Gods: The Remarkable Story of Risk by Peter L. Bernstein
The Seeds of Fiction by Bernard Diederich, Richard Greene
Weird Space 2: Satan's Reach by Eric Brown
Death on the Mississippi by Forrest, Richard;