Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis (649 page)
Authors: Mary A. Williamson Mt(ascp) Phd,L. Michael Snyder Md

BOOK: Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis
7.93Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
Interpretation
Increased In
The luteal phase of menstruating women and pregnancy, during which it rises.
When defective 21-alpha hydroxylase and 11-beta hydroxylase are present.
The most common form of CAH, where deficiency of the enzyme 21-hydroxylase blocks normal synthesis of cortisol, leading to a compensatory increase of ACTH secretion; this results in increased levels.
Limitations
Circulating normally exhibits a diurnal pattern similar to that of cortisol, with higher values in the early morning than in the late afternoon. Hence, the time of collection should be standardized.
Spuriously elevated levels are sometimes seen in premature and sick newborns due to interference with other steroid metabolites. 17α-Hydroxypregnenolone sulfate (percent cross-reactivity: 3.8%) has been identified as the most significant interferent in direct assays.
17α-Hydroxyprogesterone values for women with late-onset CAH have been found to overlap with those encountered in hirsute, oligomenorrheic women who do not have the disorder. Accordingly, it is important to determine ACTH-stimulated 17α-hydroxyprogesterone levels in women suspected of having late-onset CAH.
17-KETOSTEROIDS, URINE (17-KS)
Definition
17-Ketosteroids, urine (17-KS), are breakdown products of androgens and are an adrenal function test. Examples of 17-KS include androstenedione, androsterone, estrone, and dehydroepiandrosterone. An alternative and more specific test for adrenal androgen function is dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate in serum.

Normal range:
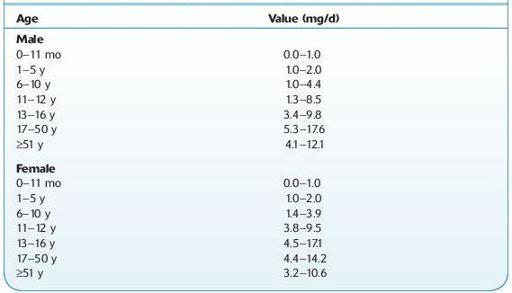
depends on sex and age (Table 16.2).
TABLE 16–2. Normal Ranges for 17-Ketosteroids in the Urine
Use
Other books
Nerds Who Kill: A Paul Turner Mystery by Mark Richard Zubro
Acts of Violets by Kate Collins
Ambassador 4: Coming Home by Jansen, Patty
Cat's eye by Margaret Atwood
London Calling by Karen Booth, Karen Stivali
A May-September Wedding by Bill Sanderson
Mala hostia by Luis Gutiérrez Maluenda
First Down (Texas Titans #3) by Cheryl Douglas
Resurgent Shadows (Successive Harmony Book 1) by Nielsen, Kevin L.