Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis (796 page)
Authors: Mary A. Williamson Mt(ascp) Phd,L. Michael Snyder Md

BOOK: Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis
13.69Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
Adults: WBC 0–5 cells/mm
3
, RBC 0/mm
3
Newborns: WBC 0–30/mm
3
, RBC 0/mm
3
TABLE 16–17. Differential Counts for CSF (Mean ± SD)
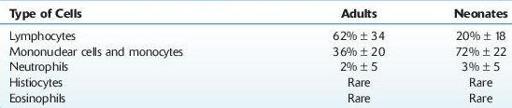
*Submitted By Liberto Pechet, MD.
Use
Examination of CSF is required when CNS involvement by inflammatory, infectious, neoplastic, or neurologic complications are suspected. Up to 20 mL of fluid can be removed in the adult.
CSF is divided into three sterile tubes:
Chemistry and immunology studies
Microbiology examinations
Cell count, differential, and cytology (if indicated)
Interpretation
Increased number or red blood cells: either hemorrhagic tap or subarachnoid hemorrhage
Increased number of neutrophils: bacterial or early viral CNS infection, early CNS TB, CNS syphilis, fungal infection, contamination with peripheral blood through traumatic tap, CNS hemorrhage
Increased number of lymphocytes: viral infection of the CNS, CNS TB, acute lymphocytic leukemia or lymphoma of the CNS, cryptococcal infection of the CNS, fungal infection of the CNS, CNS syphilis, parasitic disease infecting the CNS, Guillain-Barré syndrome
Other books
Command Decision by Haines, William Wister
Living with the Dead by Kelley Armstrong
Servant of the Bones by Anne Rice
Radiance (Wraith Kings Book 1) by Grace Draven
Prince - John Shakespeare 03 - by Rory Clements
Peril at Somner House by Joanna Challis
The Promise by Weisgarber, Ann
Sing for the Dead (London Undead) by Schnyder, PJ
Massacre in West Cork by Barry Keane
How To Salsa in a Sari by Dona Sarkar