Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis (866 page)
Authors: Mary A. Williamson Mt(ascp) Phd,L. Michael Snyder Md

BOOK: Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis
11.63Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
Following diagnostic cardiac catheterization or cardiac pacemaker unless myocardial injury is sustained during the procedure.
IM injections (total CK may be slightly increased).
Seizures (total CK may be markedly increased).
Brain infarction or injury (total CK may be increased).
Limitations
The presence of CK-MB is not unequivocally specific for myocardium, because it is found in patients with muscular dystrophies, polymyositis, hypothermia and hyperthermia, uremia, DKA, and septic shock. Renal failure, tissue damage following surgery, and cardiac contusion may also cause an elevation of CK-MB.
Cardiac troponin is the preferred marker for the diagnosis of MI. CK-MB by mass assay is an acceptable alternative when cardiac troponin is not available.
Suggested Readings
Apple FS, Preese LM. Creatine kinase-MB: Detection of myocardial infarction and monitoring reperfusion.
J Clin Immunoassay.
1994;17:24–29.
Gibler WB, Lewis LM, Erb RE, et al. Early detection of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with chest pain and nondiagnostic ECGs: Serial CK-MB sampling in the emergency department.
Ann Emerg Med.
1990;19(12):1359–1366.
CREATININE CLEARANCE (CrCl)
Definition
This test compares the creatinine in a 24-hour sample of urine to the creatinine level in the blood to show how much blood the kidneys are filtering out each minute. It is calculated by the formula:
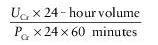
where
U
Cr
is urine creatinine,
P
Cr
is plasma creatinine

Normal range:
Male: 90–139 mL/minute
Female: 80–125 mL/minute
Other books
Temptation by Nora Roberts
Sally Singletary's Curiosity (The Sally Singletary Book 1) by J.M. Cataffo
Wild Aces by Marni Mann
La rabia y el orgullo by Oriana Fallaci
Find, Fix, Finish by Peritz, Aki, Rosenbach, Eric
Seaview Inn by Sherryl Woods
The Rift Rider by Mark Oliver
Sexting Curves (BBW Erotic Romance) by Wick, Christa
The Curse of Crow Hollow by Billy Coffey
The House at Sandalwood by Virginia Coffman