Financial Markets Operations Management (36 page)
Read Financial Markets Operations Management Online
Authors: Keith Dickinson

We have seen in a previous chapter that most markets support one or more central securities depositories. We therefore have a situation where the investor that owns securities has them ultimately held by a local/domestic CSD. In this section we will look at the intermediaries that stand between the investor and the CSD and explore the interrelationships between them in the following three circumstances:
- Custody in a local market.
- Custody in the global markets.
- Custody in the EuroMarkets.
This custody model can be applied when the investor owns securities issued in his own market. The investor has three possible choices, he can:
- Appoint a custodian to act on his behalf regardless of how many brokers he chooses to use; or
- Hold his securities in his broker's participant account at the CSD; or
- It might be possible for the investor to open a direct securities account with the local CSD.
In the majority of cases, the custodian is likely to be a bank. If we take Canada as an example, a Canadian-based investor might use CIBC Mellon or RBC as their custodian bank.
Figure 10.2
illustrates the investorâcustodianâCSD links.
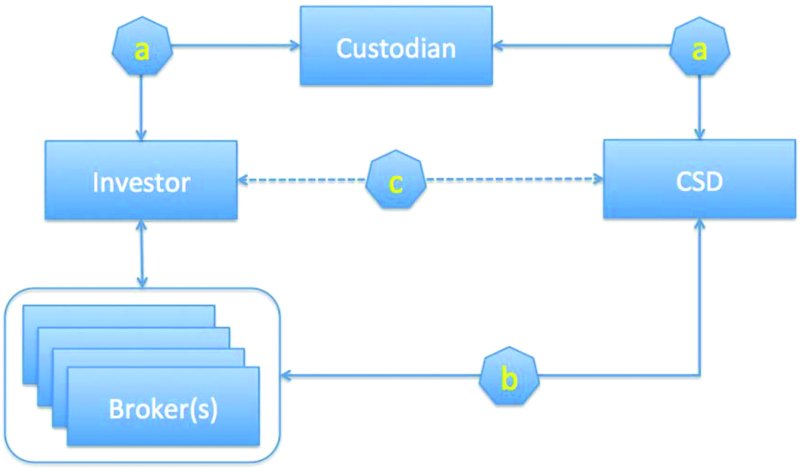
FIGURE 10.2
Local market
Although each of these three choices has its own advantages and disadvantages, it makes sense to make use of a local custodian and/or local brokers and/or the local CSD. These arrangements certainly work well when most, if not all, of the investor's securities are locally based.
What might the situation be if the investor has securities held, say, in two or three different markets? The investor could very well apply the same “local” model in each of the markets. The same advantages and disadvantages would apply but the time and effort required to manage these relationships would be more demanding. For example, there would be additional considerations, including:
- The need for appropriate legal agreements in each of the markets;
- The need to understand the workings of the markets (whilst similar, there will be technical differences);
- The potential difficulties in collating information from more than one market;
- Time zone problems and different deadlines;
- Possible language issues.
All of these will require the investor to actively manage different relationships. If these markets are located in the same region, there is an opportunity to consolidate the custodian situation, as shown in
Table 10.7
. Conversely, if these markets are located in different regions, then the local market model might be the most appropriate.
TABLE 10.7
Regional custody
| Region | Countries |
| North America and the Caribbean | Bermuda, Canada, Mexico and USA |
| Latin America | Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, Peru, Uruguay and Venezuela |
| Europe, Middle East and Africa (EMEA) | Countries on and close to the Greenwich Meridian, i.e. from Iceland to the UAE to South Africa |
| Asia-Pacific | From Russia and India to the west of the region through China, Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, etc. to Japan and South Korea to the east of the region. This region might also include Australia and New Zealand; if not, see below. |
| Australasia | Australia and New Zealand |
In the situation where the investor happens to be based, for example, in Brazil and chooses to invest in a few of the other Latin American countries, he might choose a Brazilian custodian that has links to the custodians in the other countries, as shown in
Figure 10.3
.
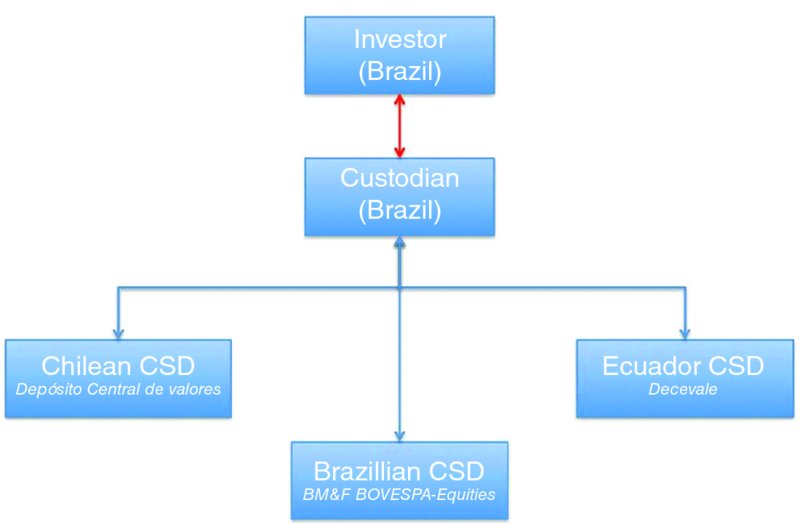
FIGURE 10.3
Local markets in the same region (the brokers have been removed for reasons of clarity)
In this scenario, the investor maintains a single relationship with his local custodian. The Brazilian custodian, in the role as a regional custodian, maintains links with the local CSD in Brazil and the foreign CSDs in Chile and Ecuador.
Now we can consider an institutional investor that is globally invested. Its choices, as we have seen above, might be to:
- Appoint a local custodian in each and every market that it invests in. This could be in the region of 100+ markets; or
- Appoint regional custodians in North and Latin America, EMEA, Asia-Pacific and Australasia (i.e. five custodians).
Either way, the investor has a challenging set of relationships to manage. One solution is to appoint a single custodian that manages a network of local custodians located in the countries in which most investors choose to invest.
The single custodian is known as a
global custodian
and the individual local custodians are known as
sub-custodians
(or
agent banks
). Collectively, we refer to this as
global custody
.
A global custodian was defined by the International Securities Services Association (ISSA)
1
in 1990, as follows:
It should be noted that the client and its global custodian do not have to be in the same country.
The global custodians are typically banks that offer a range of services including securities services. For example, Northern Trust's Asset Servicing includes the following headline services:
2
- Collateral and liquidity management;
- Cross-border pooling;
- Execution services;
- Fund services;
- Global custody;
- Investment operations outsourcing;
- Securities lending;
- Transition management;
- Treasury services.
Gauging the size of the business is difficult, but it is estimated that the key figure, assets under custody (AUC), exceeds USD 140 trillion, with the top ten global custodians holding around 80% of this. The top five global custodians are shown in
Table 10.8
.
TABLE 10.8
Assets under custody
| Rank | Provider | AUC (USD Billions) |
| 1 | BNY Mellon | 27,900 |
| 2 | J.P. Morgan | 21,000 |
| 3 | State Street | 20,996 |
| 4 | Citi | 14,500 |
| 5 | BNP Paribas | 8,986 |
Source:
© 2014 globalcustody.net. Reproduced with consent. Extract from:
www.globalcustody.net
as at Wednesday, 16 July 2014.
As you will observe in
Figure 10.4
, the client has one relationship to manage; this is with the global custodian. For the global custodian, in addition to its clients, it has to manage its network of sub-custodians, each of which represents the entry point into the relevant market (e.g. clearing systems and CSDs).
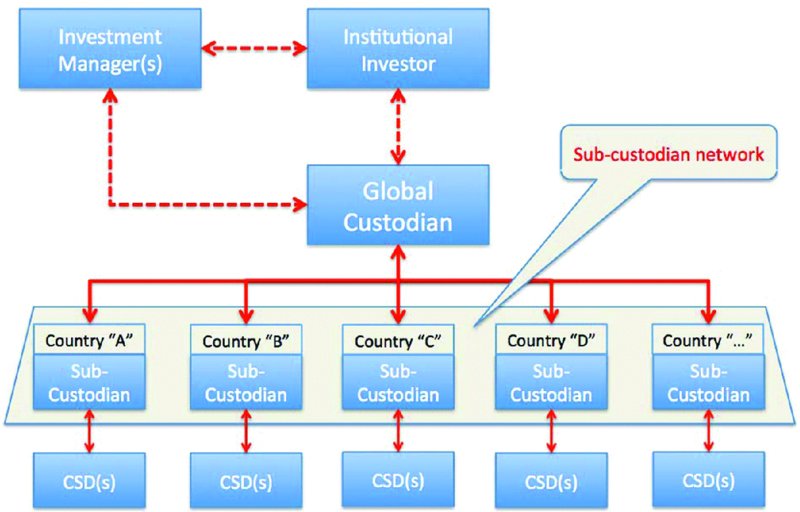
FIGURE 10.4
Global custody structure: sub-custodian network
The network consists of banks that operate in a particular market and whose clients are the global custodians. Please note that the same banks can act as local custodians, as explained above.
An example of a sub-custodian network is that of HSBC Securities Services
3
in
Table 10.9
.
TABLE 10.9
HSBC Securities Services acting as a local custodian
| Region | Countries |
| Asia-Pacific (in 16 countries) | Australia, Bangladesh, China (Shanghai and Shenzhen), Hong Kong SAR, India, Indonesia, Japan, Malaysia, New Zealand, Philippines, Singapore, Sri Lanka, South Korea, Taiwan, Thailand and Vietnam. |
| Europe (in 7 countries) | Cyprus, Germany, Greece, Kazakhstan, Malta, Turkey and United Kingdom. |
| Americas (in 4 countries) | Argentina, Bermuda, Brazil and Mexico. |
| Middle East and North Africa (in 11 countries) | Bahrain, Egypt, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Mauritius, Oman, Palestine, Qatar, Saudi Arabia and United Arab Emirates. |
In addition to HSBC Securities Services, other banks that act as sub-custodians in multiple locations include:
- Citi
- BNP Paribas
- Deutsche Bank
- Standard Chartered Bank.
The main types of institutional investor that purchase global custody services tend to be:
- Investment managers (including sovereign wealth funds and hedge funds), who use external custodians to handle their client business across the globe.
- Institutional investors (e.g. pension funds, insurance companies and charities):
- Pension funds can be self-invested but are more likely to use investment managers. Using a global custodian can ensure that information is consolidated by the custodian on behalf of the pension fund.
- Insurance companies use external custodians to handle their client business across the globe.
- Pension funds can be self-invested but are more likely to use investment managers. Using a global custodian can ensure that information is consolidated by the custodian on behalf of the pension fund.
- Institutional funds (e.g. mutual funds, sicavs, hedge funds, private equity funds, etc.), which use external custodians to handle their business across the globe.
- Custodian banks looking to appoint sub-custodian agents in those markets where the global custodian does not have suitable branches. It is therefore likely that some global custodians will choose to use competitor banks as sub-custodians.
It is possible to consider the relationships between institutional clients, investment managers and the global custodian banks from two points of view. In both cases, information (e.g. transaction instructions submitted to the custodian and reports submitted by the custodian) is exchanged between the investment manager and the custodian. The question remains as to who is the actual client of the custodian: is it the investment manager or is it the institutional client?
The institutional client appoints one or more investment managers (at “A”) and the custodian (at “C”); it can arrange for its investment manager(s) to communicate with the single custodian (at “B”), as shown in
Figure 10.5
. This has the advantage that the custodian is totally involved with all the investment managers and can report on a consolidated basis back to the institutional client.
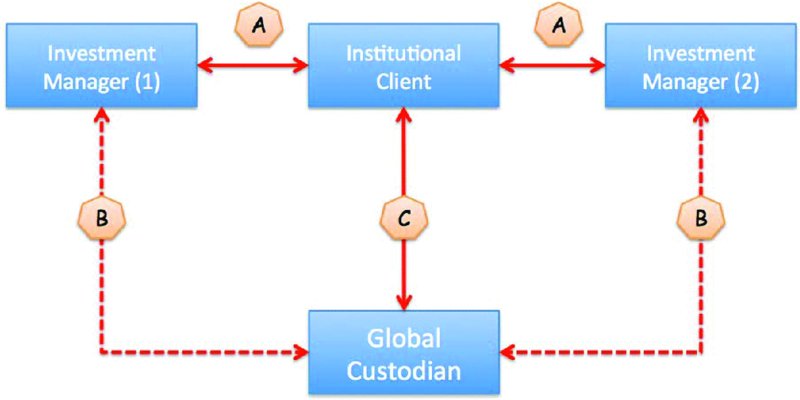
FIGURE 10.5
Institutional client appoints global custodian
In terms of a day-to-day operational relationship, the investment managers are quasi-clients of the custodian, although the latter's fees are charged back to the institutional client.
For any investment manager involved in this type of arrangement, there is one disadvantage and that is the likelihood that the investment manager will be dealing with several global custodians, each one having been appointed by the investment manager's client. That can make it challenging for the investment manager to manage so many relationships.
The investment client appoints the investment manager, as above (at “A”). However, as an alternative to the above arrangement, it is possible for the investment manager to appoint its own choice of global custodian (at “B”) and thus the institutional client just has a single relationship to manage, i.e. with its investment manager. The choice of global custodian remains solely with the investment manager, as shown in
Figure 10.6
.
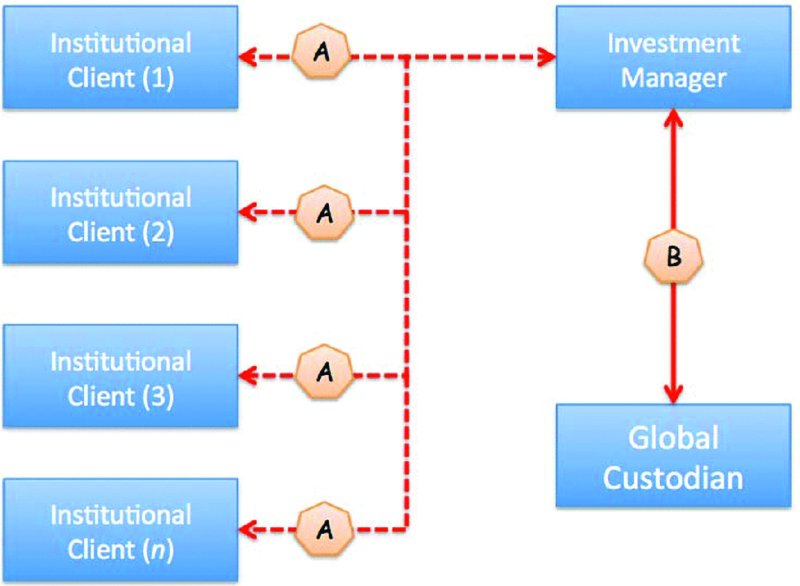
FIGURE 10.6
Investment manager appoints global custodian
The advantage for the investment manager is perhaps clear to see; it is able to deal with the global custodian of its choice and not have to be concerned with managing a network of global custodial relationships. The disadvantage for the institutional clients is that they cannot benefit from some of the compliance-related services offered by the global custodian.
If we can regard the services offered by the clearing systems and CSDs (and to a lesser extent by the sub-custodians) as being wholesale-based, we can think of the services offered by the global custodians as being more retail-based. Let us take settlements as an example; for a CSD, a transaction will settle when both the asset and cash are available. This can be regarded as wholesale. The global custodian will attempt to make the settlement look better than it really is; it will attempt to add value to the client. We will see how this can be achieved below.
The global custodian is therefore acting as an intermediary between the owner and the market infrastructure and, at the same time, adding a degree of value for the benefit of the owner.
The types of service offered by the global custodians can be divided into two groups:
- Basic services.
- Value-added services.
Not every client will want or need all of the services on offer, but it is generally the case that most clients will require the basic services. Clients may not need or may not be permitted to take some of the value-added and related services; it depends entirely on each client's situation.
Nevertheless, global custodians are innovators and will constantly seek to develop services and products that clients might be interested in taking.
- Basic services (see
Table 10.10
). - Value-added services (see
Table 10.11
).
TABLE 10.10
Basic services
| Basic Services | Comments |
| Client service | The day-to-day servicing of a client's accounts, including the resolution of problems and queries as they arise. |
| Relationship management | The overall custodian/client working relationship, including decisions on product development, policies and agreements. |
| Clearing and settlement | Ensuring timely settlement of securities transactions, chasing fails and managing outstanding items. |
| Securities safekeeping | Provision of pooled and/or segregated custody accounts, reconciling clients' positions. |
| Income collection | Collecting dividends and coupons and ensuring that the correct amounts are received. Claiming entitlements on failed cum-dividend transactions. |
| Corporate actions | Taking responsibility for the completeness, accuracy and timeliness of pre-advice corporate action data that are available in local markets and submitting instructions for voluntary events. |
| Proxy voting/class actions | Notification of meeting types, dates, resolutions and some information on votes and results, in the appropriate language. Arranging for clients' voting decisions to be relayed to the issuer and handling class actions where appropriate. |
| Cash management | Sweeping and pooling of cash balances. Management of cash surpluses through either investment in liquid funds using the custodians' own products or via a third party. |
| Foreign exchange | Quoting competitive exchange rates and enabling clients to execute trades on-screen in all tradable currencies, 24 hours a day. |
| Withholding tax services | Reclaims in markets that have tax treaties and exemptions. |
| Recordkeeping and reporting | Providing multi-currency reporting on clients' securities and cash positions, along with transaction status. Includes regulatory and specialist reporting. |
| Technology | Communications via SWIFT, custodians' proprietary systems and web-based information delivery. |
| Network management | Access to (and management of) global network of sub-custodians in anywhere from 70 to more than 100 markets. Adding new markets and evaluating and providing information about the risks involved are important to both fund managers and institutional investors. |
| Market information | Financial market profiles (operating regulations, systems and procedures in local markets, etc.). Commenting on infrastructure risks in capital markets, evaluating CSD risk. Market surveillance and risk monitoring. |
TABLE 10.11
Value-added services
| Value-Added Services | Comments |
| Securities lending | Enhancing overall portfolio performance by offering a managed, fully collateralised securities lending programme. |
| Investment accounting | Accounting and reporting for investment funds. Includes preparing financial statements (balance sheet, changes in equity, income statements and cash flows), earnings per share, NAV per share, financial instrument disclosures, etc. |
| Pricing and valuation | Obtaining and verifying local market prices, revaluing securities and translating into clients' base currencies. Includes listed and unlisted securities. |
| Performance measurement | Monitoring funds' performance against benchmarks and providing insights into that performance. Analytics include investment strategy performance by geography, investment type and industry, as well as benchmarking against other managers and market indices. |
| Derivatives clearing | Transaction processing for both ETD and OTC derivatives through the custodians' global clearing member status. This includes the centralisation of clients' positions and margin payments. Custodians manage collateral and provide an independent pricing service for non-cleared OTC derivatives. |
| Fund administration | Accounting and administration for onshore and offshore collective investment programmes. |
| Transition management | Minimise the costs and risks associated with asset reallocation. |
| Commission management | Help to reduce commission exposure through effective transaction cost control. |
| Compliance management | Monitor compliance with clients' investment guidelines. Provide an independent check of clients' compliance with market regulations and investment guidelines. |