Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis (529 page)
Authors: Mary A. Williamson Mt(ascp) Phd,L. Michael Snyder Md

BOOK: Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis
13.86Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
Immune complex–mediated diseases (typically show hypocomplementemia): for example, IgA nephropathy, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), acute postinfectious GN, membranoproliferative GN
Cell Mediated
Examples include Wegener granulomatosis, polyarteritis.
Infectious
Acute poststreptococcal (group A beta-hemolytic GN)
Non-poststreptococcal: bacterial (e.g., infective endocarditis, bacteremia), viral (e.g., HBV, HCV, CMV infections), parasitic (e.g., trichinosis, toxoplasmosis, malaria), or fungal
Noninfectious
Multisystem (e.g., SLE, Henoch-Schönlein purpura, Goodpasture syndrome, Alport syndrome)
Primary glomerular disease (e.g., IgA nephropathy, membranoproliferative GN)
Hypocomplementemic
Intrinsic renal diseases (especially poststreptococcal, membranoproliferative GN)
Systemic (e.g., SLE, cryoglobulinemia)
Normocomplementemic
Intrinsic renal diseases (e.g., IgA nephropathy, idiopathic rapidly progressive GN)
Systemic (e.g., polyarteritis nodosa, Wegener granulomatosis)
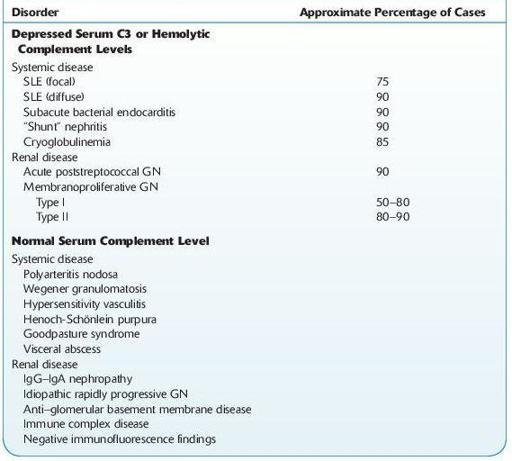
See Table
12-4
.
TABLE 12–4. Serum Complement in Acute Nephritis
Various Clinical Courses of GN
Other books
A Wilderness So Immense by Jon Kukla
Privy to the Dead by Sheila Connolly
The Stolen Crown: The Secret Marriage That Forever Changed the Fate of England by Susan Higginbotham
My Trip Down the Pink Carpet by Leslie Jordan
The Ghost of Crutchfield Hall by Mary Downing Hahn
Spirit Lake by Christine DeSmet
The View From Connor's Hill by Barry Heard
Scare the Light Away by Vicki Delany
Bingo Brown's Guide to Romance by Betsy Byars