Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis (526 page)
Authors: Mary A. Williamson Mt(ascp) Phd,L. Michael Snyder Md

BOOK: Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis
10.48Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
Urinalysis
Microscopic examination is an important tool in determining the etiology of CKD. WBCs, RBCs, and casts are usually found.
Dipstick examination for albumin, glucose, pH, nitrate, and blood contribute to determining the etiology of CKD.
Blood pH measurement can be helpful since acidosis is a frequent complication of advanced CKD.
Serum abnormalities include hyperphosphatemia, hyperkalemia, hyponatremia, hypocalcemia, and hypermagnesemia. Uric acid and amylase may also be increased.
Hypoalbuminemia and hyperlipidemia (increased triglycerides, cholesterol, and VLDL lipoprotein levels) may occur, and they are common in the nephrotic syndrome. Hypergammaglobulinemia with monoclonal gammopathy suggests myeloma kidney as the etiology of CKD.
Anemia is caused by reduction in the synthesis of erythropoietin and usually develops with reduction of renal function to 30–50% of normal.
Coagulation studies may be affected by uremic by-products such as guanidinosuccinic acid and exuberant production of nitrous oxide by uremic vessels, resulting in abnormal platelet function.
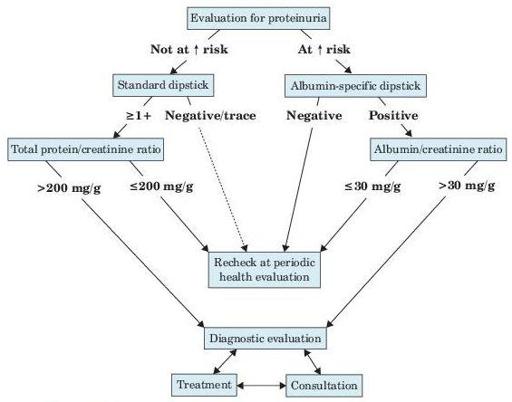
Figure 12–2
Evaluation of proteinuria in patients not known to have kidney disease.
Suggested Readings
National Kidney Foundation. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification and stratification.
Am J Kidney Dis.
2002;39(Suppl 1):S1–S266.
http://www.kidney.org/professionals/kdoqi/pdf/ckd_evaluation_classification_stratification.pdf
Stevens PE, Levin A, et al. Evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease: synopsis of the kidney disease: improving global outcomes 2012 clinical practice guideline.
Ann Intern Med.
2013;158(11):825–830.
FOCAL SEGMENTAL GLOMERULOSCLEROSIS
Definition
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) is a histologic lesion that is commonly found to underlie the nephrotic syndrome. It accounts for 20% of nephrotic syndrome cases in children and 40% of such cases in adults. In addition, it is the most common pathology identified in patients with ESRD.
Classified as
Other books
The Man in 3B by Weber, Carl
The Cutting Crew by Steve Mosby
El Río Oscuro by John Twelve Hawks
Playing For Love by J.C. Grant
Witches Anonymous by Misty Evans
Ruby Parker Hits the Small Time by Rowan Coleman
The Highlander's Hope - A Contemporary Highland Romance by MacKay, Cali
My Darrling by Krystal McLean
The Staff and the Blade: Irin Chronicles Book Four by Elizabeth Hunter
Grim Shadows (Roaring Twenties) by Jenn Bennett