Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis (703 page)
Authors: Mary A. Williamson Mt(ascp) Phd,L. Michael Snyder Md

BOOK: Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis
2.1Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
“Hyperchloremia” in bromide intoxication (if chloride determination by colorimetric method).
False increase in serum chloride or HCO
3
−
.
False decrease in serum sodium (e.g., hyperlipidemia, hyperviscosity)
Increased unmeasured cations
Hyperkalemia, hypercalcemia, hypermagnesemia
Increased proteins in multiple myeloma, paraproteinemias, polyclonal gammopathies (these abnormal proteins are positively charged and lower the AG).
Lithium and bromide overdose.
Simultaneous changes in ions may cancel each other out, leaving AG unchanged (e.g., increased Cl
−
and decreased HCO
3
−
). The change in AG should equal change in HCO
3
−
; otherwise a mixed, rather than simple, acid– base disturbance is present.
ANTIARRHYTHMIC DRUGS
See Cardiovascular Drugs.
ANTIBIOTICS
Definition
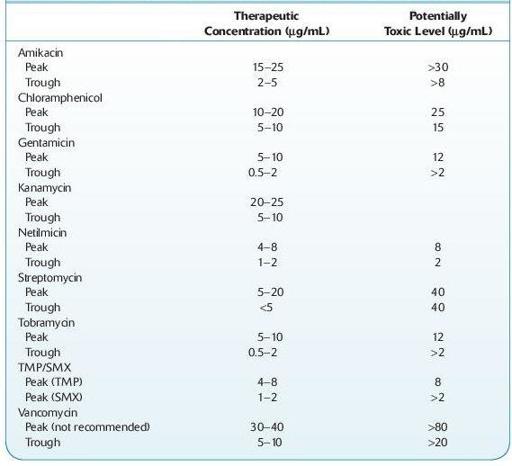
Antibiotics are substances that destroy or inhibit the growth of microorganisms. Antibiotics consist of chemical groups such as β-lactams, polyenes, macrolides, tetracyclines, aminoglycosides, and sulfonamides. Names include amikacin, chloramphenicol, gentamicin, kanamycin, streptomycin, tobramycin, and vancomycin.

Normal therapeutic (and toxic) levels:
see Table 16.5.
TABLE 16–5. Therapeutic and Toxic Serum Concentrations for Antibiotics
Use
Other books
Trail of Lust by Em Petrova
The Cupel Recruits by Willshire, Susan
Taken by the Fae Lord by Emma Alisyn
Chasing Jane by Noelle Adams
White Man Falling by Mike Stocks
The Way of the Traitor: A Samurai Mystery by Laura Joh Rowland
The Truth About Love by Sheila Athens
037 Last Dance by Carolyn Keene
The Squashed Man Who Married a Dragon by Anthony Blackie
The Beach Quilt by Holly Chamberlin