Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis (705 page)
Authors: Mary A. Williamson Mt(ascp) Phd,L. Michael Snyder Md

BOOK: Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis
3.89Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
Cardiolipins, and other related phospholipids, are lipid molecules found in cell membranes and platelets. They play an important role in the blood clotting process. When antibodies are formed against cardiolipins (ACAs against IgG, IgM, and IgA), they increase an affected patient’s risk of developing recurrent inappropriate blood clots (thrombi) in both arteries and veins.
Other names include antiphospholipid antibodies.

Normal range:
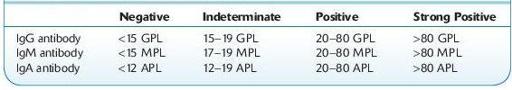
see Table 16.6.
TABLE 16–6. Normal Levels of ACAs
Use
Evaluation of suspected cases of antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (APS).
Unexplained blood clot.
Recurrent miscarriages.
ACAs are present in APS, SLE, acute infections, HIV, and certain cancers and with some drug (e.g., phenytoin, penicillin, procainamide). They occur in the general population, with the prevalence increasing with age.
Interpretation
APS is present if at least one of the clinical criteria and one of the laboratory criteria that follow are met.

Clinical criteria
Vascular thrombosis
Other books
Seducing Simon by Maya Banks
Adam Selzer by How to Get Suspended, Influence People
My Raptor: An Erotic Shapeshifting Paranormal Romance by Connor, Cara B.
The Star Plume by Kae Bell
Dating Without Novocaine by Lisa Cach
Moonlit Embrace by Lyn Brittan
Countdown by Natalie Standiford
Fire by Deborah Challinor
Naughty Nanny Series-Free Loving by Azod, Shara
Long Lost: A Kate Burkholder Short Story by Linda Castillo