Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis (709 page)
Authors: Mary A. Williamson Mt(ascp) Phd,L. Michael Snyder Md

BOOK: Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis
13.47Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
Definition
A compound used to prevent or treat seizures
Classic agents: carbamazepine (Tegretol), phenobarbital (Luminal), phenytoin (Dilantin), ethosuximide (Zarontin), valproic acid (Depakene, Depakote). Newer agents gabapentin (Neurontin), lamotrigine (Lamictal), oxcarbazepine (Trileptal), vigabatrin (Sabril), topiramate (Topamax), zonisamide (Zonegran)
Use
Treatment of seizure disorders

Normal therapeutic levels:
see Table 16.7
Limitations
Phenobarbital may be detected by immunoassay-based screening tests for barbiturates in urine and serum.
Immunoassay tests are available for semiquantitative analysis in serum of topiramate, valproic acid, phenytoin, phenobarbital (may demonstrate significant cross-reactivity with other barbiturates), and zonisamide.
Lamotrigine, breakdown products or artifacts of topiramate, carbamazepine, 10-OH-carbazepine, and phenytoin may be detected in general drug screens in urine or serum that utilize alkaline or weakly acidic liquid- or solid-phase extractions followed by gas chromatography or GC/MS analysis.
TABLE 16–7. Normal Therapeutic Levels of Anticonvulsants
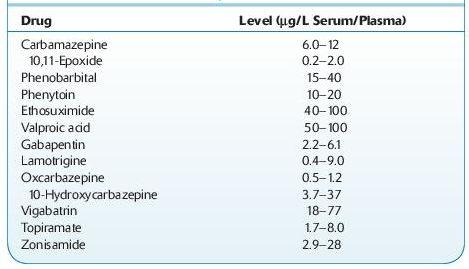
*Submitted By Amanda J. Jenkins, PhD.
For the majority of anticonvulsants, specific tests are required.
ANTIDEPRESSANTS
*
Definition
Other books
The Watch (The Red Series Book 1) by Amanda Witt
The Spirit Survives by Gary Williams Ramsey
HotTango by Sidney Bristol
Trapstar 3 by Karrington, Blake
Tomb of Zeus (Atlantis) by Christopher David Petersen
Osprey Island by Thisbe Nissen
The Fleet by John Davis
9781618853073LyricsandLustLabelleNC by Unknown
Book of Love by Abra Ebner
Trowchester Blues 01 - Trowchester Blues by Alex Beecroft