Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis (611 page)
Authors: Mary A. Williamson Mt(ascp) Phd,L. Michael Snyder Md

BOOK: Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis
2.01Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
D = decreased; I = increased; N = normal.
TABLE 13–3. Illustrative Serum Electrolyte Values in Various Conditions
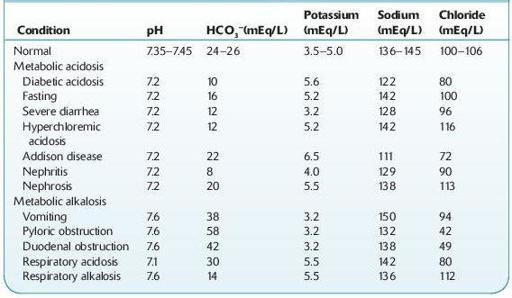
TABLE 13–4. Summary of Pure and Mixed Acid–Base Disorders
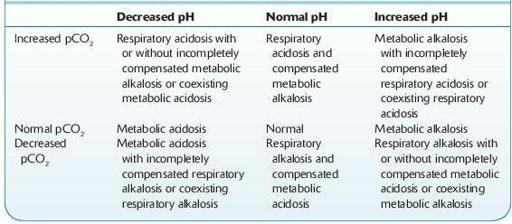
Data from Friedman HH.
Problem-Oriented Medical Diagnosis
, 3rd ed. Boston, MA: Little, Brown; 1983.
TABLE 13–5. Immediate and Delayed Compensatory Response to Acid–Base Disturbances
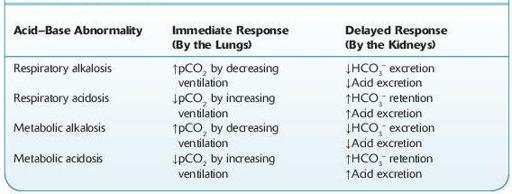
↑, increases; ↓, decreases.
TABLE 13–6. Primary Change, and Compensatory Mechanisms in Delayed Response to, and Chloride Level in AcidBase Disturbances
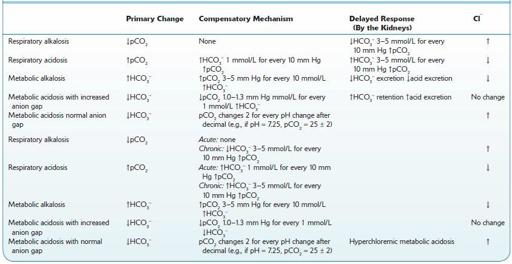
↑, increased;↓, decreased.
RESPIRATORY ALKALOSIS
Respiratory alkalosis is defined as a decreased pCO
2
of <38 mm Hg.
Caused by Hyperventilation
CNS disorders (e.g., infection, tumor, trauma, CVA, anxiety–hyperventilation)
Hypoxia (e.g., high altitudes, ventilation–perfusion imbalance, PE)
Cardiovascular (e.g., CHF, hypotension)
Pulmonary disease (e.g., pneumonia, pulmonary emboli, asthma, pneumothorax)
Drugs (e.g., salicylate intoxication, methylxanthines, β-adrenergic agonists)
Metabolic (e.g., acidosis [diabetic, renal, lactic], Cirrhosis, liver failure)
Others (e.g., fever, pregnancy, gram-negative sepsis, pain)
Other books
In Like Flynn by Rhys Bowen
The Tangling of the Web by Millie Gray
Wyoming Winterkill by Jon Sharpe
Fire and Ice by Susan Page Davis
The Matchmaker by Kay Hooper
Deadly Errors by Allen Wyler
The Mystery of the Stolen Corn Popper by David A. Adler
Baby by Patricia MacLachlan
Craving Her Curves by Nora Stone
One of the Guys by Lisa Aldin