Zero (16 page)
Authors: Charles Seife

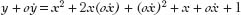
Rearranging the terms yields
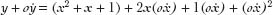
Since
y
=
x
2
+
x
+ 1, we can subtract
y
from the left side of the equation and
x
2
+
x
+ 1 from the right side of the equation and leave the system unchanged. That leaves us with
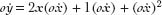
Now comes the dirty trick. Newton declared that since
o was really, really small, (
was really, really small, (
o )
)
2
was even smaller: it vanished. In essence, it was zero, and could be ignored. That gives us
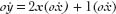
which means that
o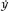 /
/
o = 2
= 2
x
+ 1, which is the slope of the tangent line at any point
x
on the curve (Figure 26). The infinitesimal time period
o
drops right out of the equation,
o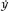 /
/
o becomes
becomes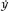 /
/ , and
, and
o
need never be thought of again.
The method gave the right answer, but Newton's vanishing act was very troubling. If, as Newton insisted, (
o )
)
2
and (
o )
)
3
and higher powers of
o were equal to zero, then
were equal to zero, then
o itself must be equal to zero.
itself must be equal to zero.
*
On the other hand, if
o was zero, then dividing by
was zero, then dividing by
o as we do toward the end is the same thing as dividing by zeroâas is the very last step of getting rid of the
as we do toward the end is the same thing as dividing by zeroâas is the very last step of getting rid of the
o
in the top and bottom of the
o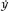 /
/
o expression. Division by zero is forbidden by the logic of mathematics.
expression. Division by zero is forbidden by the logic of mathematics.